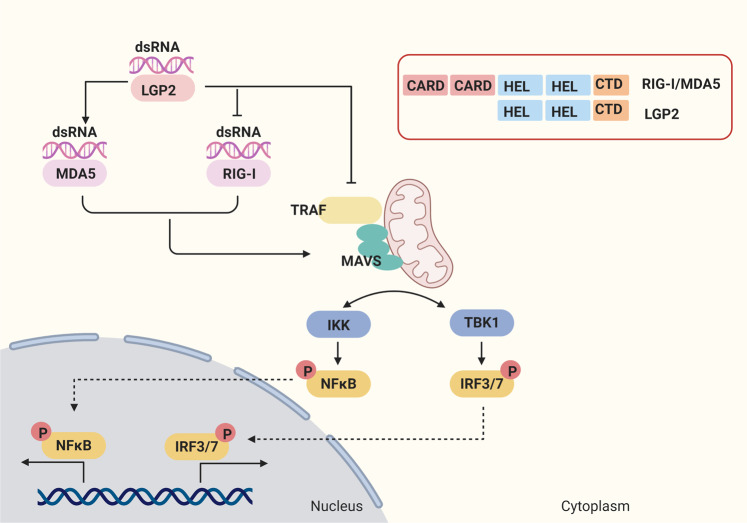
Fig. 1.
RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs) mediated signal transduction pathway. RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs) have been identified as important cytoplasmic RNA sensors, including RIG-I, MDA5, and LGP2. RLRs are common in sharing the DExD/H-box helicase domain and C-terminal domain (CTD), and RIG-I and MDA5 contain two N-terminal tandem caspase activation and recruitment domains (CARD), while LGP2 lacks CARD. RIG-I detects cytoplasmic viral short dsRNA that contains a 5′-triphosphate or 5′-diphosphate moiety, whereas MDA5 recognized long dsRNA structures. LGP2 can bind RNA ligands of RIG-I, interfering with IKK recruitment to MAVS through protein interaction or binding to RIG-I through a repressor domain directly, to inhibit the activation of RIG-I. LGP2 can increase the ability of MDA5 to form stable filaments on dsRNA to promote the MDA5- mediated pathway. LGP2 interacts with TRAF and disrupt its activity, which results in the disruption of IRFs and NFκB activation. Activated RIG-I and MDA5 induce the recruitment and polymerization of the adapter MAVS on the mitochondrial membrane. Then MAVS activates TBK1 as well as the IKK complex, which activates IRF3 and IRF7, and NF-κB. And the gene expression of IFNs, pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines is induced to defend viral and modulate the immunity