Figure 2.
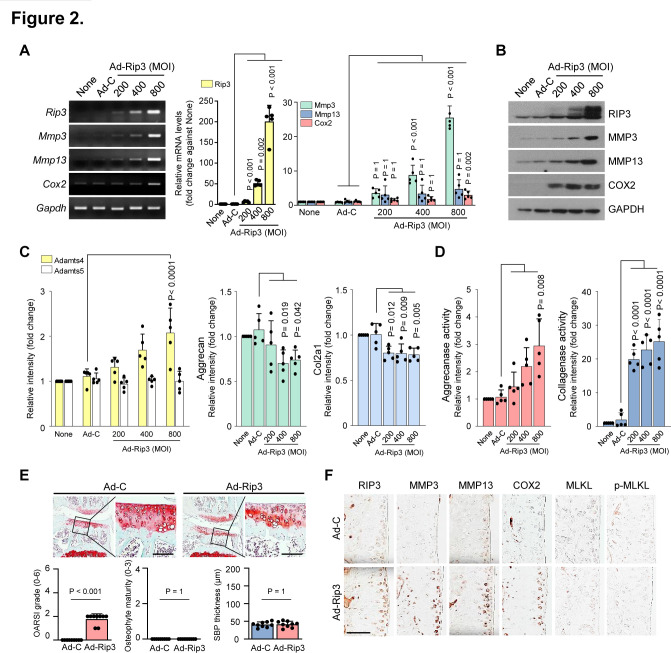
Modulation of receptor-interacting protein kinase-3 (RIP3) expression is correlated with osteoarthritis (OA). (A and B) Reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) (left), quantitative PCR (qPCR) (right) (A) and western blot (B) analysis of RIP3, matrix metalloproteinase 3 (MMP3), matrix metalloproteinase 13 (MMP13) and COX2 in chondrocytes infected with Ad-C or Ad-Rip3 at the indicated multiplicity of infection (MOI) (n=5). (C) qPCR analysis of Adamts4, Adamts5, aggrecan and Col2a1 in Ad-Rip3-infected chondrocytes (n=5). (D) Aggrecanase (left) and collagenase (right) activity by Ad-Rip3 infection in chondrocytes (n=5). (E) Cartilage destruction and OA development in mouse knee joints intra-articularly injected with Ad-C and Ad-Rip3 assessed by Safranin-O staining, Osteoarthritis Research Society International (OARSI) grading, osteophyte formation and subchondral bone plate thickness (n=9). (F) RIP3, MMP3, MMP13, COX2, MLKL and p-MLKL immunostaining in Ad-C-injected or Ad-Rip3-injected cartilage. Statistical analyses were conducted using one-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni’s test (A, C and D), non-parametric Mann-Whitney U tests (E, OARSI grading, osteophyte formation) or two-tailed t-tests (E, subchondral bone plate thickness). Scale bar: 100 μm.