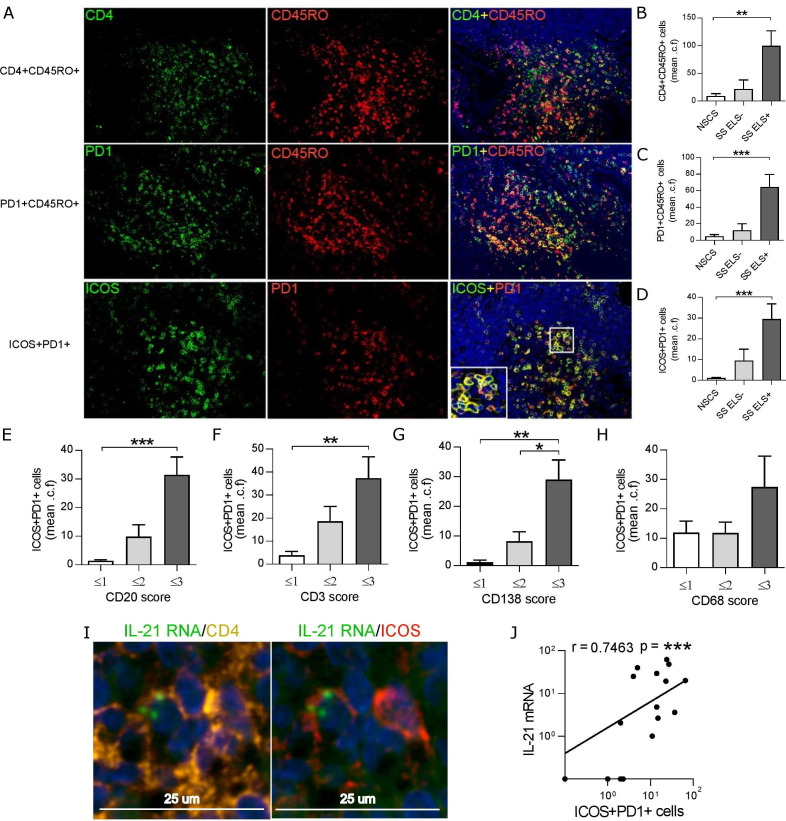
Figure 3.
PD-1+ICOS+CD45RO+CD4+ cells are increased within SG with ELS in SS and produce IL-21. (A) Representative immunofluorescence detection of CD4+CD45RO+ (top row), PD1+CD45RO+ (middle row) and ICOS+PD1+ cells (bottom row) in SG biopsy tissues with ELS. (B–D) Quantification (mean counts per field, a minimum of 5 random fields) of the double positive cells for each double immunofluorescence combination in SG biopsy tissues from NSCS (n=8) and SS (n=12) patients. Images displayed at x20 magnification. (E–H) ICOS+PD1+ cell count was segregated according to histological semi-quantitative score (0 to 3) of B (CD20), T (CD3) plasma cells (CD138) and macrophages (CD68). Statistical analysis by Kruskal-Wallis-test with Dunn’s post-test correction for multiple comparison (B–H). (I) Representative fluorescent in situ hybridisation (FISH) detection of IL-21 RNA, costained with CD4 and ICOS in SG biopsy tissues with ELS. (J) Spearman correlation analysis between SG real-time PCR IL-21 mRNA expression with ICOS+PD1+ cell count. All graphs represent mean±SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. ELS, ectopic lymphoid structure; ICOS, inducible T-cell co-stimulator; NSCS, non-specific chronic sialoadenitis; PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1; SG, salivary gland; SS, Sjogren’s syndrome.