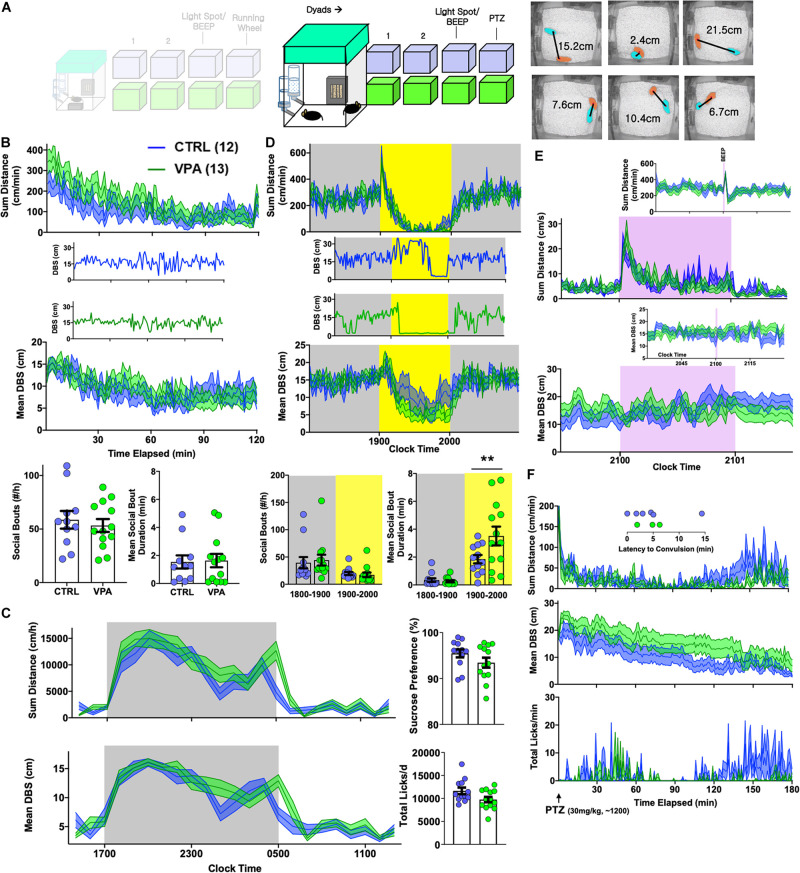
FIGURE 5.
Effects of prenatal VPA exposure on dyadic behavior. (A) Sex- and group-matched dyads were paired within BMU home cages [CTRL n = 12 pairs (7 female), VPA n = 13 pairs (8 female)]. Videotracking was used to calculate proximity (distance between subjects/DBS). (B) Continuous measures of total distance and DBS during the initial 2 h of this encounter, with representative examples of DBS. BOTTOM: Total social bouts and mean social bout durations. (C) Hourly measures of total distance and mean DBS, with average sucrose preference and total licks (day 2). (D) Light spot testing revealed greater social proximity in prenatal VPA-exposed dyads, and results of representative dyads are shown. (E) “Beep” test and (F) dynamic changes in distance, DBS and licking behavior following a 30 mg/kg PTZ injection applied to both members of the dyad, with inset depicting latency to convulsive seizures. Mean ± SEM shown for all. CTRL, control; VPA, valproic acid. ∗∗p < 0.01.