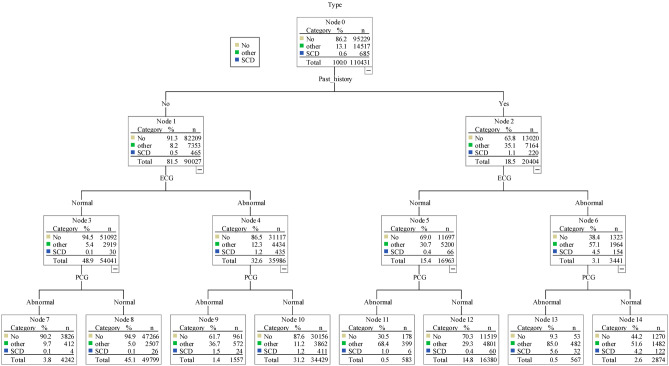
Figure 2.
Decision tree analysis of sudden cardiac death. The samples in this decision three analysis included 110,431 children. Three types of outcome variable were identified in the analysis including high risk SCD (i.e., SCD), other heart disease (i.e., other), and healthy cases (i.e., No). A total of 15,202 children referred to the hospital in the third stage were diagnosed with heart problems. These children with heart disease included 685 high risk SCD cases and 14,517 other heart disease cases. The analysis of decision tree shows that past history and simplified ECG test were two most import variables to classify these three types. In the beginning, there are 0.6% cases who were identified as high risk SCD. In the right half, for children who had past history (i.e., “Yes”), the SCD percentage increased to 1.1% (from 0.6% to 1.1%). Among those with past history “Yes”, the SCD percentage increase to 4.5% (from 1.1% to 4.5%) if their simplified ECG test are abnormal. Furthermore, among those with past history and simplified ECG test are abnormal (N = 3341), the SCD percentage increase to 5.6% (from 4.5% to 5.6%) if the simplified PCG test is abnormal. In the left half, for children who had “No” past history (N = 90027). The percentage of high risk SCD is about 0.5% (N = 465). However, if simplified ECG test is abnormal, the percentage of high risk SCD increase to 1.2%. If the both simplified ECG test and simplified PCG test are abnormal, the high risk SCD increase further to 1.5% (N = 24). The children without past history and normal initial simplified ECG results, simplified PCG test has little benefit in identifying high risk of SCD (0.1% to 0.1%). For the 26 students without past history and normal initial simplified ECG and simplified PCG results, they were referred for further examination because the pediatric cardiologist judged the PCG result was abnormal in 4, the ECG result was abnormal in 19, and 7 students had abnormal physical examination. The diagnoses of these 26 students included hypertrophy cardiomyopthy 1 case, WPW syndrome 11 cases, and long QT syndrome 14 cases. Note: “Other” indicates other heart disease. “No” indicates non-high risk of SCD. “SCD” indicates high risk of SCD. The adjusted p < 0.01 for all comparisons. ECG, electrocardiogram; PCG, phonocardiograph; SCD, sudden cardiac death.