Fig. 3.
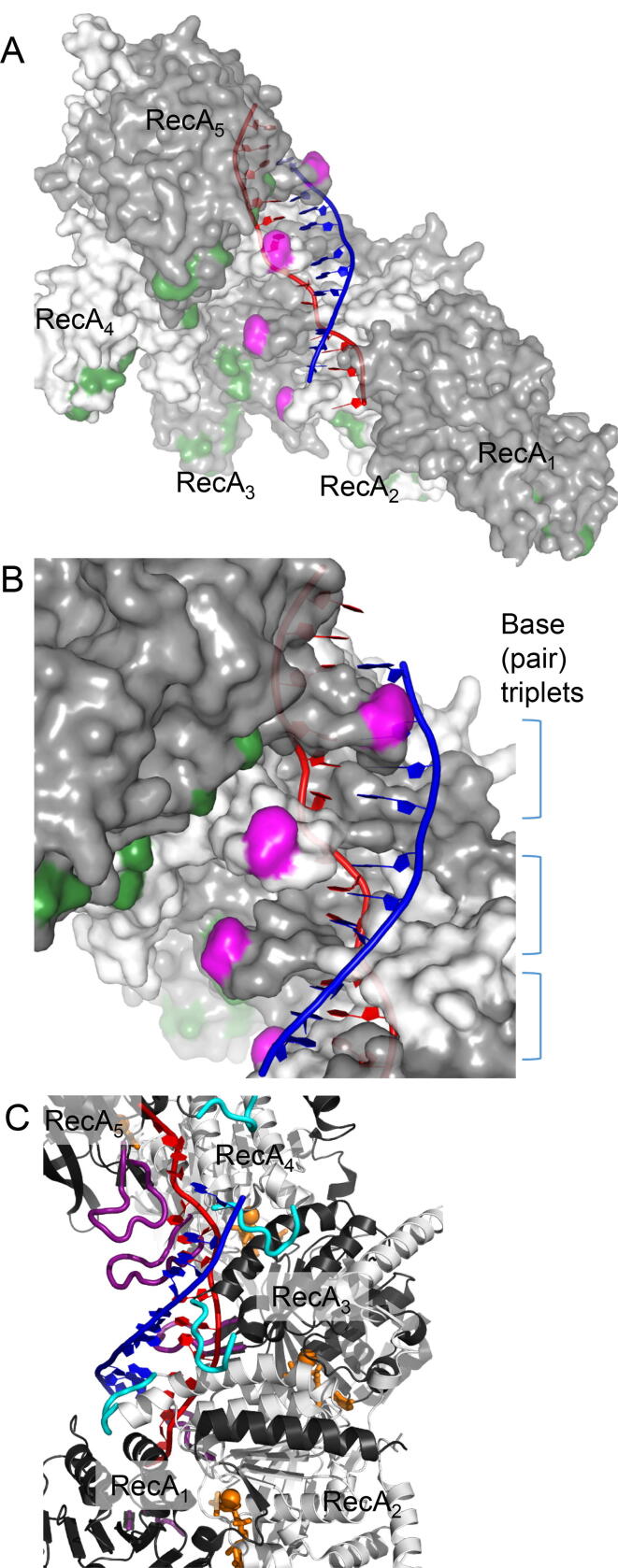
Crystal structure of active RecA-DNA filament. These panels show the 5 RecA protomers of 6 protomers per a turn of an elongated (i.e., active) RecA spiral filament containing dsDNA, which is likely to represent the hybrid duplex after D-loop formation [42] (PDB: 3CMX). The 3D structures of the RecA filament and the ssDNA in the RecA-ssDNA complex are almost identical to those of the RecA-filament and the red strand of the dsDNA in the RecA-dsDNA complex, respectively [42]. The blue strand is another strand of the dsDNA. After homologous-complex formation, the blue strand represents a strand of dsDNA paired with invading ssDNA in the hybrid duplex. A. Side view from the inside of the spiral filament. Basic amino acid residues consisting of gateway are colored green. B. Close-up of base triplets and L2 loops of which top is colored in magenta. C. ATP (analogue) molecules bound between two adjacent RecA protomers. Non-hydrolysable ATP analogues and Mg2+ ions are shown in orange. L1 and L2 loops are shown in cyan and purple, respectively. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)