figs3.
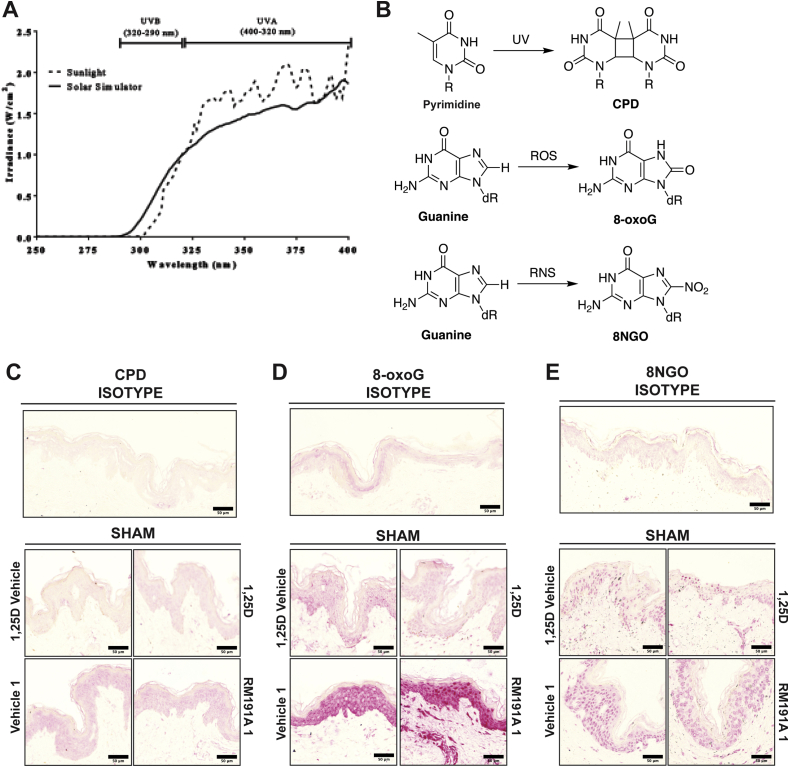
Figure S3: RM191A protects against UV-induced oxidative stress and DNA damage
(A) A comparison of the output of natural sunlight with the Oriel 450W solar simulator containing an atmospheric attenuation filter. The dotted line represents the output of natural sunlight at midday in October in Sydney, Australia, while the solid line represents the output of the solar simulator used in all experiments in human explant skin. While the output of the solar simulator closely resembles that of natural sunlight, the former emits 10% UVB, while the latter emits 5% UVB. (B) Schematic diagram showing the formation of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPD), 8-oxo-guanine (8-oxoG) and 8-nitroguanine (8NGO). (C) Representative images of immunohistochemical staining of CPDs in human explants from isotype control and sham exposed explants. There was little staining in the isotype control. Sham irradiated skin showed low levels of nuclear staining. (D) Representative images of immunohistochemical staining of 8-oxoG in human explants from isotype control and sham exposed explants. (E) Representative images of immunohistochemical staining of 8NGO in human explants from isotype control and sham exposed explants.