Fig. 7.
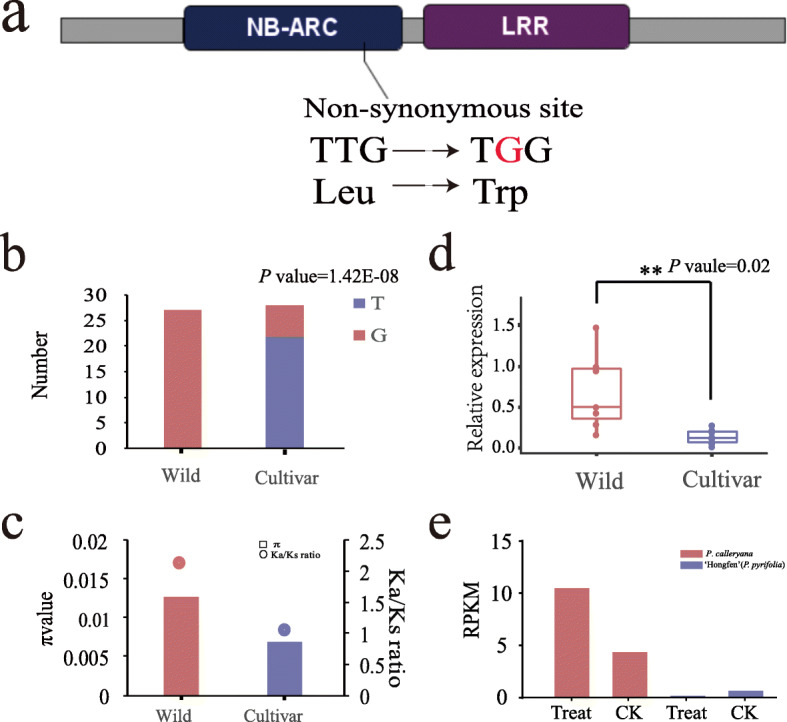
Divergence of Pbr025269.1 between Asian cultivated and wild groups. a One significantly different non-synonymous SNP located on NBS domain. b Genotyping distribution of SNP1 in Asian cultivated and wild groups (chi-square test, p-value = 1.42E-08). c Ka/Ks ratio and nucleotide diversity of Pbr025269.1 in Asian wild and cultivated groups. Bars mean nucleotide diversities and spots mean Ka/Ks ratios. d Expression profiles of Pbr025269.1 in ten Asian cultivated (PyL2, PyL7, PyL8, PyL9, PyL10, PyL11, PyI1, PyI9, PyI11, PyI14) and seven Asian wild (PyW5, PyW6, PyW7, PyW9, PyW12, PyW13, PyW14) pear accessions at enlarged stage by RT-qPCR analysis. The relative expression levels of each individual NBS-encoding genes were normalized by the Pyrus GAPDH gene. The expression level of PyW14 sample was used as a reference (relative expression level = 1). Each point means relative expression level of one pear accession. ‘**’ means significant difference (T-test, p-value< 0.05) between wild and cultivated groups. (e) RPKM value of Pbr025269.1 in P. calleryana and ‘hongfen’ pear (an Asian cultivate pear), ‘Treat’ means inoculated A. alternata groups and ‘CK’ means control groups; red represents P. calleryana, blue represents ‘hongfen’(P. pyrifolia)
