Figure 1.
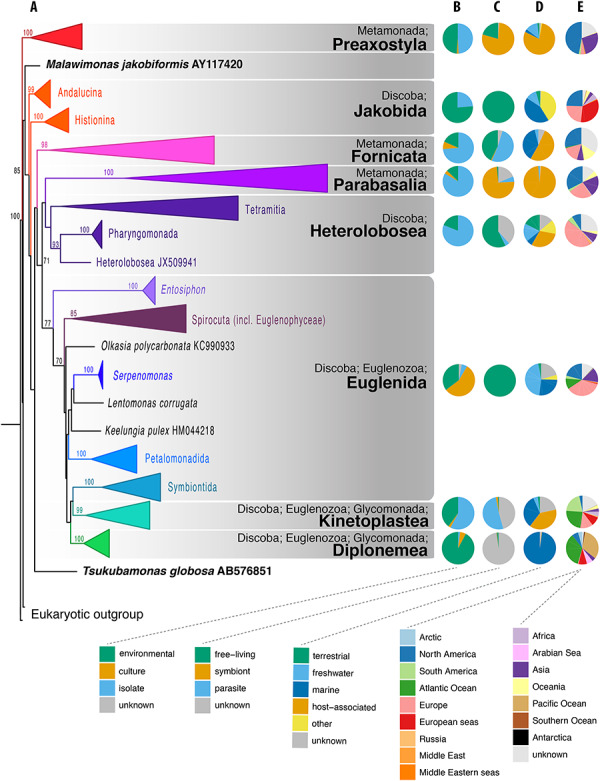
Phylogenetic and compositional overview of the Excavata EukRef databases. (A) Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of SSU sequences in the Excavata database. Monophyletic clusters corresponding to deep-level taxa within the Excavata were collapsed at their common ancestral nodes when strongly supported by bootstrapping. The tree was constructed using a GTRCAT nucleotide substitution model. Bootstrap values are shown at nodes with at least 70% support. (B–E) Pie charts showing the proportion of sequences for metadata categories for each Excavata database. (B) Source of the organism from which the SSU sequence was derived. ‘Environmental’ indicates sequences obtained from the DNA of bulk environmental samples. ‘Culture’ indicates sequences obtained from organisms grown in culture and in culture collections. ‘Isolate’ indicates sequences obtained from organisms isolated from the environment, either as single cells or in enrichments, but not from established cultures (C) Biotic relationship of the organism. Symbiont consists of organisms with mutualist or commensal relationships, (D) Environment from which the organism was sampled, (E) Geographical location of sampled environment.
