Figure. LOX is a novel target for AAA.
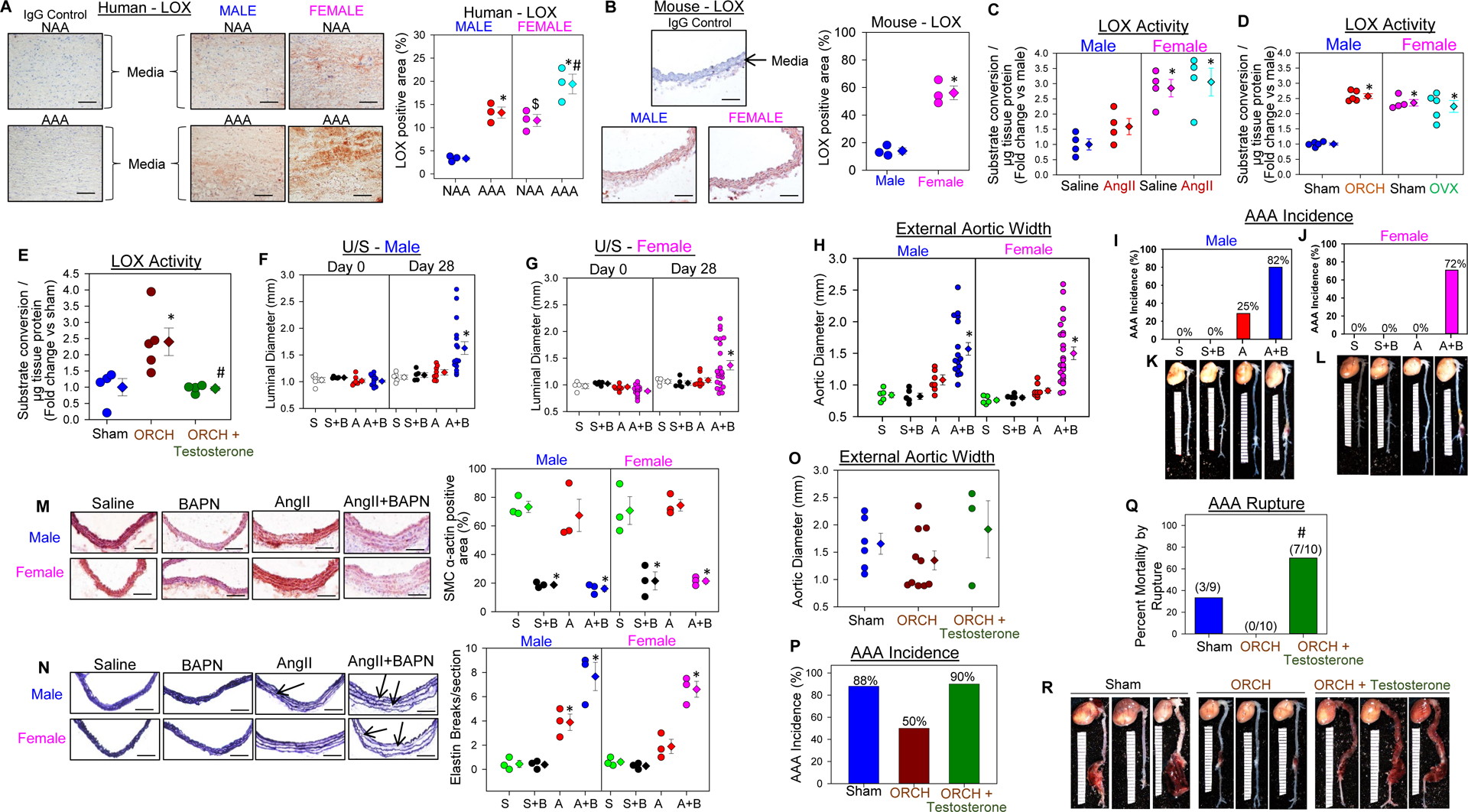
A, Immunohistochemical staining revealed LOX protein is more abundant in the media of female human non-aneurysmal and aneurysmal abdominal aortic sections (Red color indicates positive immunostaining; Abcam, ab31238; N=3, *P<0.05 AAA vs NAA; $ P<0.05 Female NAA vs Male NAA; #P<0.05 Female AAA vs Male AAA; Two-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak post hoc test). B, LOX protein is more abundant in aortic media of female mouse abdominal aortic sections compared to male (N=3, *P<0.05 female vs male; Student’s t-test). C, Aortic LOX activity is lower in male mice infused with either saline or AngII (1,000 ng/kg/min for 5 days) compared to female mice (Abcam, ab112139; N=4, *P<0.05 female vs male; Two-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak post hoc test). D, Orchiectomy (ORCH), not ovariectomy (OVX) increased aortic LOX activity in mice (N=5, *P<0.05 vs male-sham; Two-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak post hoc test). E, Testosterone replacement suppressed aortic LOX activity in ORCH mice (N=4–5, *P<0.05 ORCH vs sham; # ORCH + Testosterone vs ORCH; One-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak pairwise multiple comparison test) F&G, LOX inhibition by BAPN (0.15g/kg/day) accelerated 28 days infusion of AngII-induced aortic luminal dilation measured by ultrasound (Vevo 2100) in female mice as similar to male mice (N=5–25, *P<0.05 AngII+BAPN vs Saline/BAPN/AngII; Two-way Repeated Measures ANOVA). H-L, LOX inhibition accelerated AngII-induced AAA formation and incidence in female mice as similar to male mice (N=5–25, *P<0.05 AngII+BAPN vs Saline/BAPN/AngII; Two-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak post hoc test). M&N, LOX inhibition resulted in loss of medial SMCs (α-SMC actin staining; Abcam, ab5694) along with AngII-induced aortic medial elastin breakage (Verhoeff’s staining) equivalently in both male and female mice (N=3, *P<0.05 vs male/female Saline; Two-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak post hoc test). Scale bars correspond to 50 μm (200x magnification). O-R, BAPN administration accelerated AngII-induced AAA formation in ORCH mice and testosterone replacement significantly promoted AngII+BAPN- induced AAA rupture in ORCH mice (N=9–10, # P<0.05 ORCH + Testosterone vs ORCH; One-way ANOVA and Fisher Exact test).
