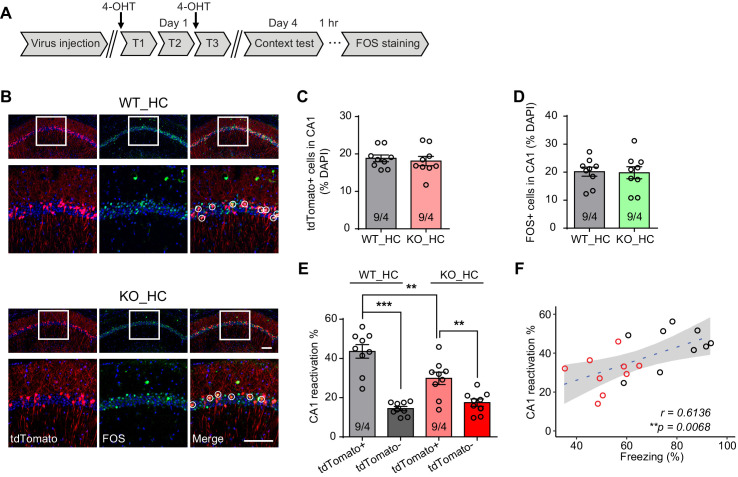
Figure 2. Reduced engram reactivation efficacy is correlated with impaired contextual fear memory in Fmr1 KO mice.
(A) Experimental protocol for activity-dependent genetic labeling of neural ensembles. Intensive fear conditioning training was used in constitutive Fmr1 KO mice to facilitate labeling. (B) Representative images showing memory-encoding neural ensembles (engram cells) labeled with tdTomato (red) and memory recall-activated neurons labeled with FOS immunostaining (green). The circles in zoomed in images highlight reactivated neurons (yellow). Scale bar: 100 μm. (C) Quantification of percentage of neurons activated during learning. (D) Quantification of percentage of neurons activated during memory recall. (E) Quantification of engram reactivation efficacy in CA1 as percent FOS-positive neurons in tdTomato-positive and tdTomato-negative populations [one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test: F (3, 32)=26.57, p<0.0001, ***p<0.001; **p<0.01]. (F) Positive correlation between neural ensemble reactivation efficacy and behavioral perform during context memory test (**p<0.01, Pearson correlation coefficient). n/N, number of mice/number of independent litters. All graphs represent mean ± SEM.