Fig. 1.
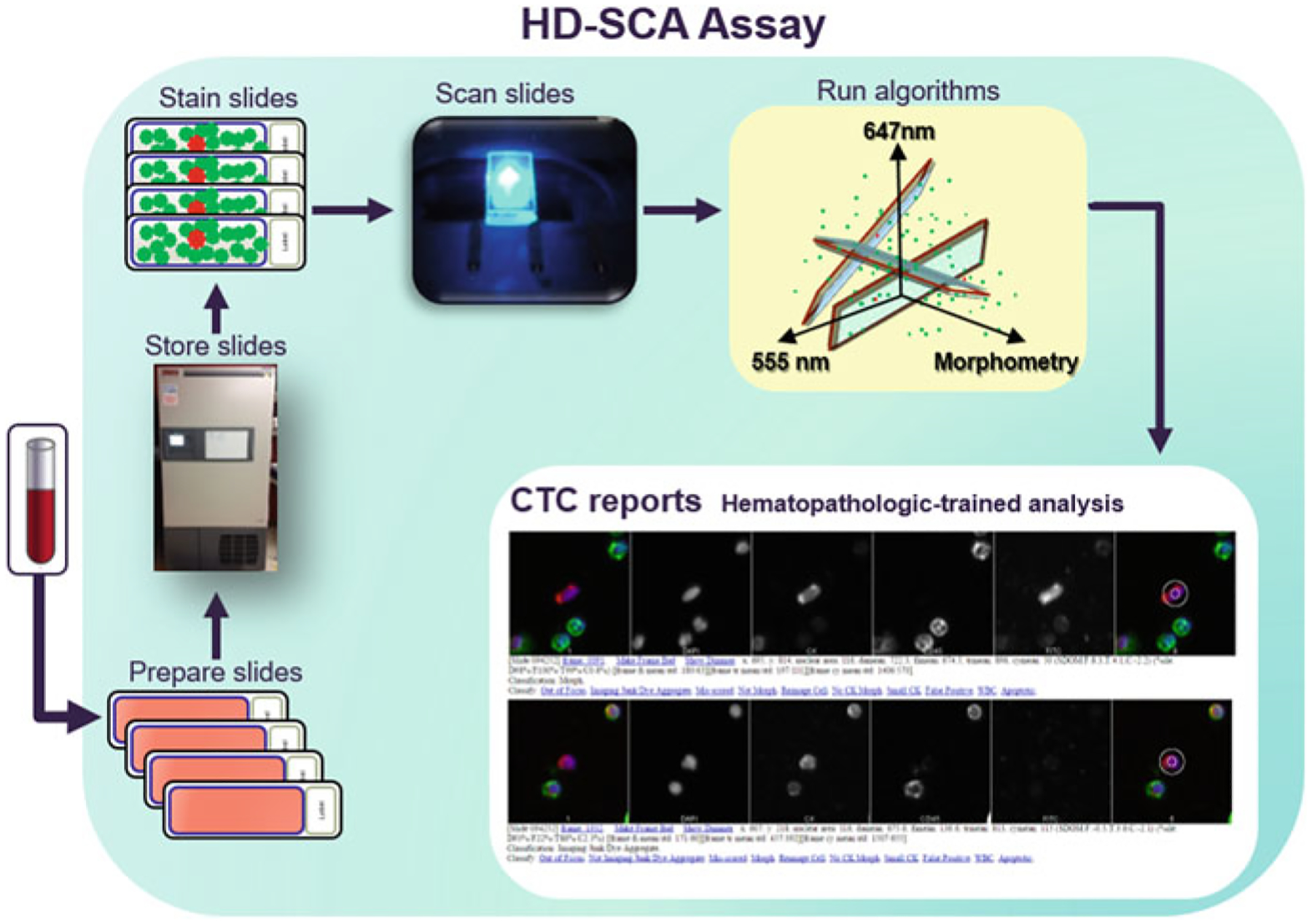
A schematic overview of the HD-SCA workflow. Received patient whole blood is treated with erythrocyte lysis and then plated onto adherent slides. Multiple slides (from the same patient draw) are kept and preserved in a biorepository until analysis is desired. This provides researchers with the ability to assay the same sample using several strategies at any time. When slides are ready to be assayed, they are immunofluorescently stained and imaged via automated scanning microscopy. The resulting images are computationally analyzed to infer candidate CTCs, which are then presented in reports for classification by a hematopathology-trained specialist
