Fig. 1.
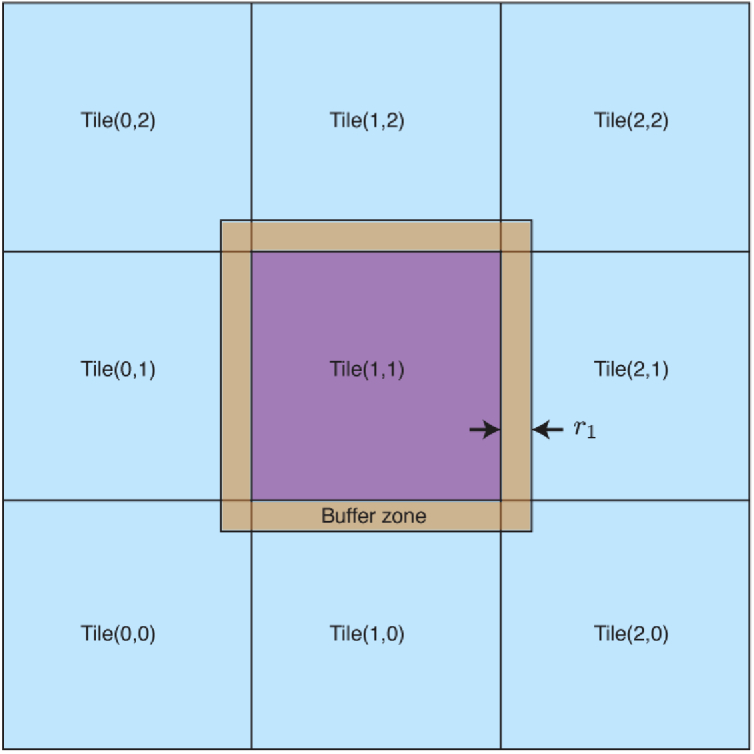
For tiling-based short-distance Fresnel multislice, one can use a tiling approach to split a large 2D array of dimension into a set of smaller arrays, each of size , so that these smaller arrays can be processed on separate computational nodes. When doing so, one must add a buffer zone of physical width (Eq. (14)), and pixel width (Eq. (15)), to each side of the tile with information from neighboring tiles. This accounts for diffraction from features at the edge of nearby tiles coming into the field of view of the tile being processed.
