Fig. 12.
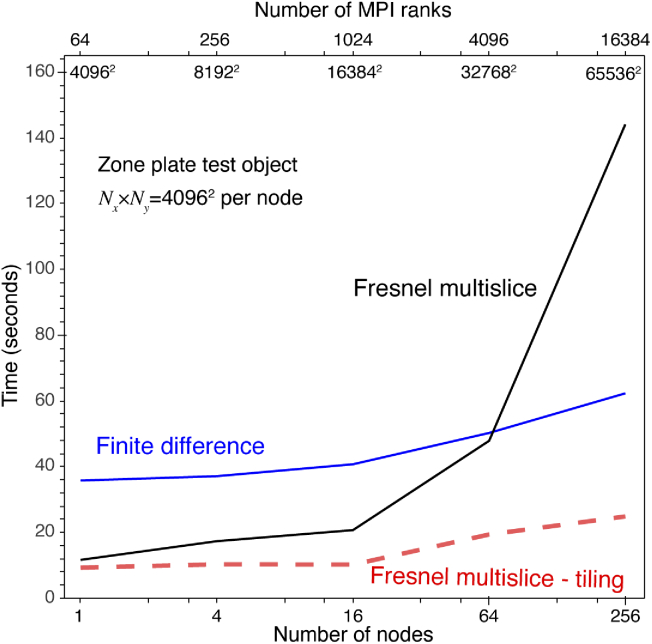
Time for calculating the exit wave for the zone plate test object as a function of increasing the transverse array size along with the number of nodes, with each node given a transverse grid size of (leading to a net array size of for 256 nodes, as indicated just below the top of the plot). For each algorithm, the number of slices was as required for convergence to the error tolerance of Eq. (28), giving values of that were in all cases within 1 or 2 slices of the values shown in Fig. 9. This “weak scaling” test shows that both the finite difference and tiling-based short-distance Fresnel multislice approaches scale well as the problem size increases with the number of nodes used, consistent with the “strong scaling” test results of Fig. 10. With the full-array Fresnel multislice approach, the time required for data communication between nodes for full-array FFTs means that even with many nodes available large problems require considerably more time to compute.