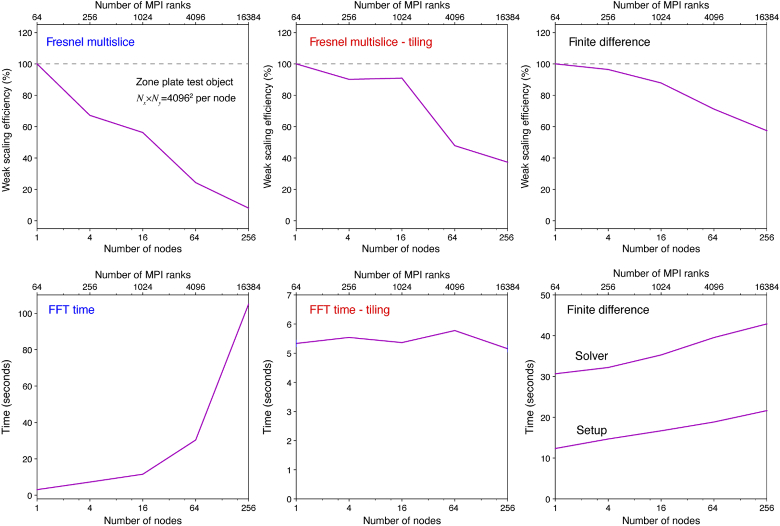
Fig. 13.
Further details on the “weak scaling” test results shown in Fig. 12. These tests were of the zone plate test object with a constant array size of per node, leading to a net array size of for 256 nodes. The top row shows the scaling efficiency for each of the three algorithms, which is the completion time compared to the 1 node result divided by the number of nodes used. The bottom row shows the time for key operations in each method: a fast Fourier transform or FFT for the Fresnel multislice approaches, and problem setup and solution for the finite difference method. As can be seen, the full-array Fresnel multislice approach has especially poor “weak scaling” performance due to the need for internode communcation at each slice position, while the tiling-based short-distance Fresnel multislice approach offers better parallel performance. The finite difference approach takes a longer time, but with less of a decrease in efficiency for larger transverse array size.