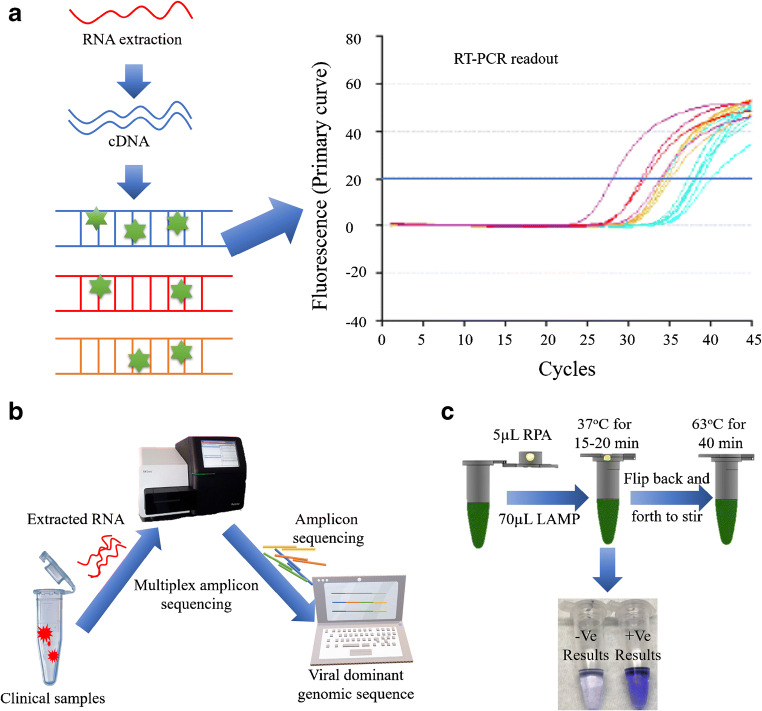
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation for the promising techniques generally used to detect SARS-CoV-2: (a) RT-PCR method is carried out from the reverse transcription of viral RNA into cDNA which is then amplified using specific primers. The amplification process is confirmed from the fluorescent signal indicating the total number of copies in target sequence. (b) Whole genomic sequencing is a complete gene sequencing method which is complicated and not helpful for urgent and large-scale detection. Generally, the viral RNA is extracted from the specimen going through multiplex amplicon sequencing to identify the nucleic acid [58]. Redrawn with permission. (c) Combined method of LAMP and COVID-19 Penn-RAMP: The Penn-RAMP contains two processes of isothermal amplification, first the RPA was carried out at 37 °C at the cap of the tube and then the LAMP at 63 °C within the tube. The LAMP reaction mixture was added with the LCV dye and the ratio between RPA and LAMP was 1:9. This was incubated at 38 °C for 15–20 min followed by flipping for through mixing moving towards second time incubation in a thermal cycler for 40 min at 63 °C. LCV dye helped by producing dark violet signal in the presence of dsDNA and colourless in the absence of dsDNA. This method was found to have high potential as it reduced false negatives [59]. Re-produced, permission has taken under the CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 International license)