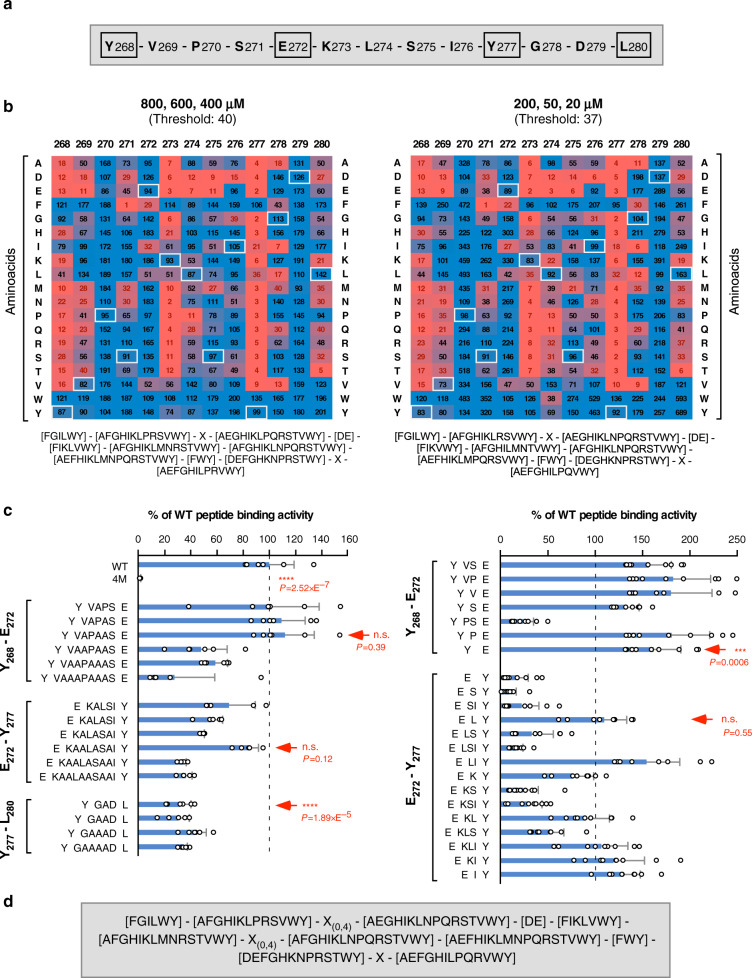
Fig. 1. WDD-binding motif refinement.
a WDD-binding peptide present in TMEM59 intracellular domain (268–280). Critical motif positions are marked by squares. b Peptide microarray studies to identify permissive aminoacids for WDD binding. Arrays containing the indicated peptide mutants were developed with GST-HA-ATG16L1231–607 to obtain crude binding values. Heatmaps display binding data expressed as the average percentage of the wild-type binding activity that is retained by each mutant. Left and right heatmaps show average data from assays performed at high (800, 600, 400 nM) and low (200, 50, 20 nM) ligand concentrations, respectively (3 experimental points, n = 8; statistics in Supplementary Fig. 1a). The color scale stretches continuously from low (red) to high (blue) binding activity. The indicated threshold values were arbitrarily established as the average binding activity displayed by variants that inhibit the interaction beyond 5%. Black/red figures indicate values above/below the threshold, thus establishing permissive/prohibited substitutions, respectively. White squares indicate native aminoacids in the wild-type peptide. Permissive residues for all positions are displayed below the heatmaps. c Microarray studies to establish the distance flexibility between critical residues. Microarrays including peptides with the indicated increased (left) or decreased (right) distances between Y268-E272, E272-Y277, and Y277-L280 were developed as in a. 4 M indicates a control peptide where critical residues are mutated to alanine (Y268A, E272A, Y277A, L280A). Shown are average binding activities processed as in a (−/+ s.d.). Data originate from 2 (left; 800, 400 nM (n = 6) except for E272-Y277 where n = 5) or 3 (right; 800, 600, 400 nM; n = 9) experimental points (n.s: P > 0,05; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001, two-sided Student’s t-test). Arrows indicate data defining the maximal (left) and minimal (right) distances allowed for each stretch. Thus, peptides YVAPAASE (Y268-E272) and EKAALASAIY (E272-277) (left), or YE (Y268-E272) and ELY (E272-277) (right), fully retain WDD-binding activity, indicating that 6 and 8 residues (left), or 0 and 1 (right), respectively, are permitted. Minimal variations in Y277-L280 spacing (YGADL; left) inhibit binding, so the native 2-residue distance was considered critical and deletions were not tested. d Inclusive WDD-binding motif integrating permissive residues and distance flexibility.