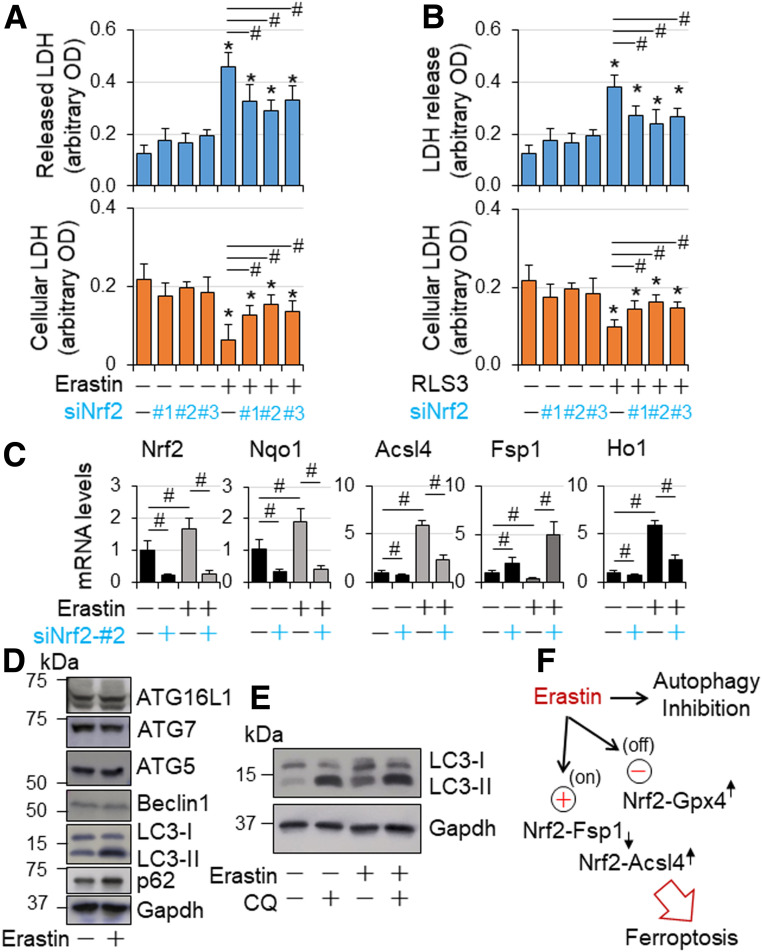
Figure 7.
Nrf2-mediated ferroptosis in H9C2 cardiomyocyte-like cells. A and B: The effect of Nrf2 knockdown on ferroptosis in H9C2 cardiomyocyte-like cells. H9C2 cells transfected with siCtl and siNrf2 RNAs as described in Fig. 6C were treated with or without erastin (5 µmol/L) and RSL3 (5 µmol/L) as indicated in serum-free DMEM for 24 h and then subjected to cytotoxicity assay as described in research design and methods. n = 4. *P < 0.05 vs. vehicle-treated groups; #P < 0.05 between indicated groups. C: The effect of Nrf2 knockdown on mRNA expression of Nrf2, Nqo1, Fsp1, and Acsl4 in a setting of GPX4 inactivation in H9C2 cardiomyocyte-like cells. H9C2 cells transfected with siCtl and siNrf2 RNAs as described in Fig. 6D were treated with or without erastin (5 µmol/L) as indicated in serum-free DMEM for 24 h and then subjected to qPCR analysis of mRNA expression as described in research design and methods. n = 4. #P < 0.05 between indicated groups. D: The effect of erastin on protein expression of autophagic genes in H9C2 cardiomyocyte-like cells. Subconfluent H9C2 cells were treated with or without erastin (5 µmol/L) in serum-free DMEM for 24 h and then subjected to Western blot analysis as described in research design and methods. The results are representatives of four separated experiments. E: The effect of erastin on autophagic flux in H9C2 cardiomyocyte-like cells. Subconfluent H9C2 cells were treated with or without erastin (5 µmol/L) in serum-free DMEM for 24 h, and chloroquine (200 µmol/L) was added during the last 2 h of culture. Autophagic flux was assessed by Western blot analysis as described in research design and methods. The results are representatives of four separated experiments. F: A working hypothesis. In a setting of GPX4 inaction and autophagy inhibition, such as erastin treatment, Nrf2 drives the expression of ferroptosis executor Acsl4 while suppressing the expression of ferroptosis inhibitor Fsp1, thereby promoting ferroptosis in cardiomyocytes.