FIGURE 3.
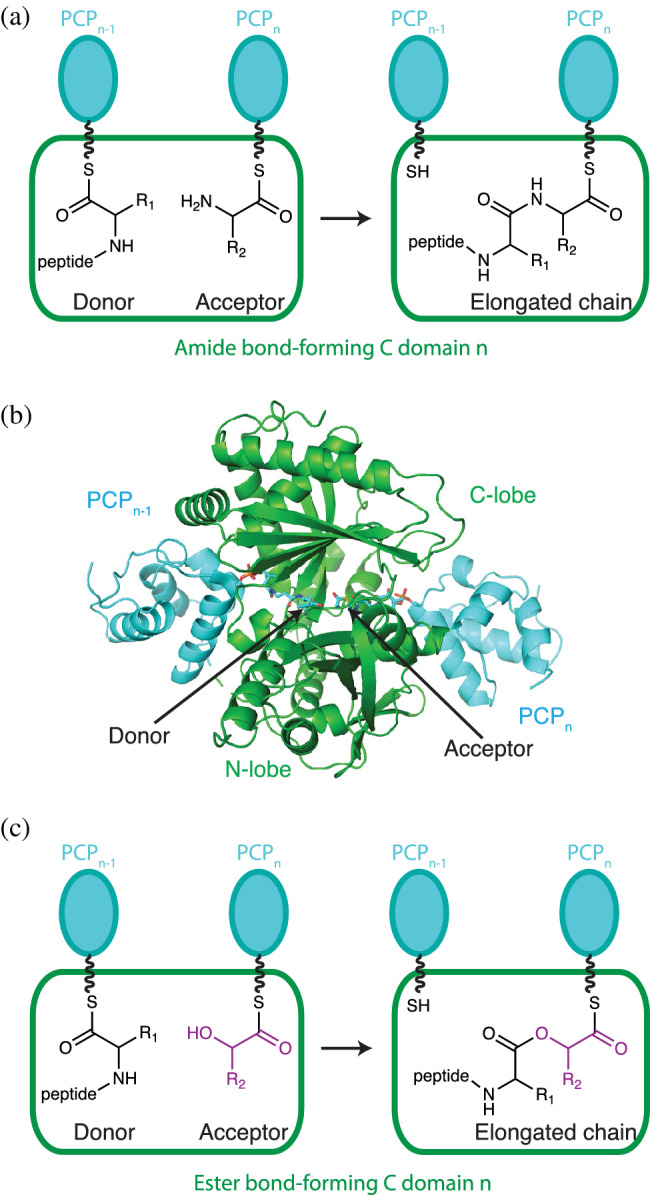
The condensation domain catalyzes amide and/or ester bond formation (a) Amide bond formation occurs in the active site of a condensation domain (green rectangle). Substrates are presented as thioesters attached to phosphopantetheine (wavy line) in PCP domains (cyan). The PCP in the preceding module (n − 1) relays the donor substrate, while the acceptor substrate resides in the current module (n). (b) Structure of condensation conformation of the C domain with acceptor and donor PCP domains, extracted from the dimodular NRPS LgrA. 97 The domain has N‐terminal and C‐terminal lobes which each have chloramphenicol acetyl transferase‐like folds. Donor peptidyl‐ppant and acceptor aminoacyl‐ppant are attached to PCP domains (cyan). (c) Some condensation domains can form ester bonds using OH groups as nucleophiles
