FIGURE 12.
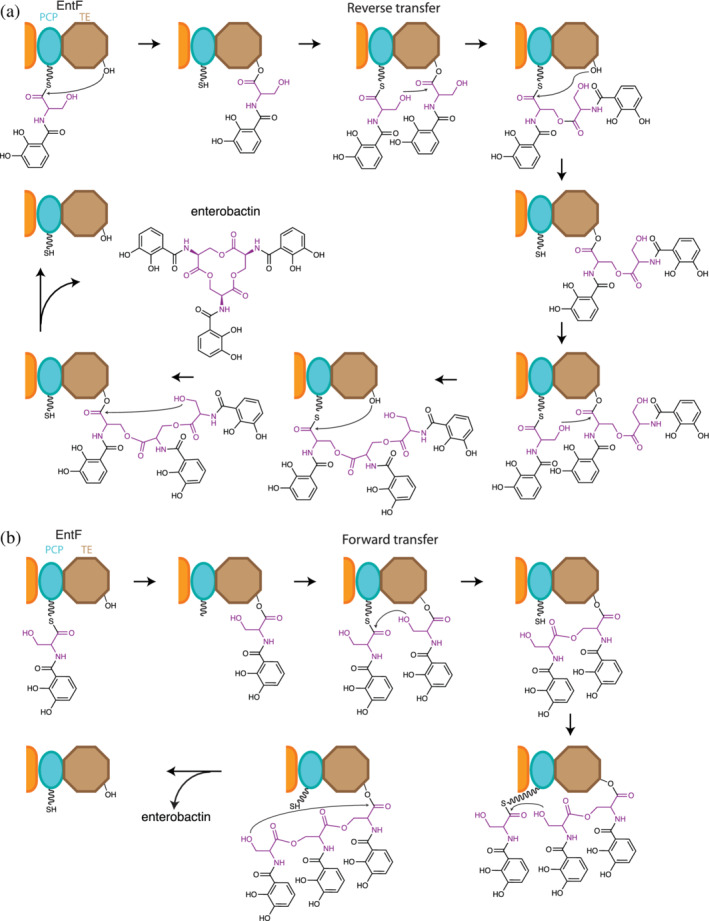
Two proposed oligomerization mechanisms for EntF TE. In both scenarios DHB‐Ser‐S‐PCP is formed on EntF and is transferred to its TE domain, generating DHB‐Ser‐O‐TE. From there, the pathways differ. (a) Reverse transfer oligomerization pathway: A newly made DHB‐Ser‐S‐PCP attacks DHB‐Ser‐O‐TE, forming (DHB‐Ser)2‐S‐PCP. This is transferred to the serine of the TE domain. When a third DHB‐Ser‐S‐PCP is made, another multistep cycle of this oligomerization mechanism takes place to make (DHB‐Ser)3‐S‐PCP and transfer it to the TE domain, giving (DHB‐Ser)3‐O‐TE. (b) Forward transfer oligomerization pathway: DHB‐Ser‐O‐TE attacks the incoming DHB‐Ser‐S‐PCP to make (DHB‐Ser)2‐O‐TE directly. When a third DHB‐Ser‐S‐PCP is made, another iteration of the single step mechanism occurs to make (DHB‐Ser)3‐O‐TE. In both pathways the TE domain releases enterobactin by cyclization of the (DHB‐Ser)3 of (DHB‐Ser)3‐O‐TE
