FIGURE 13.
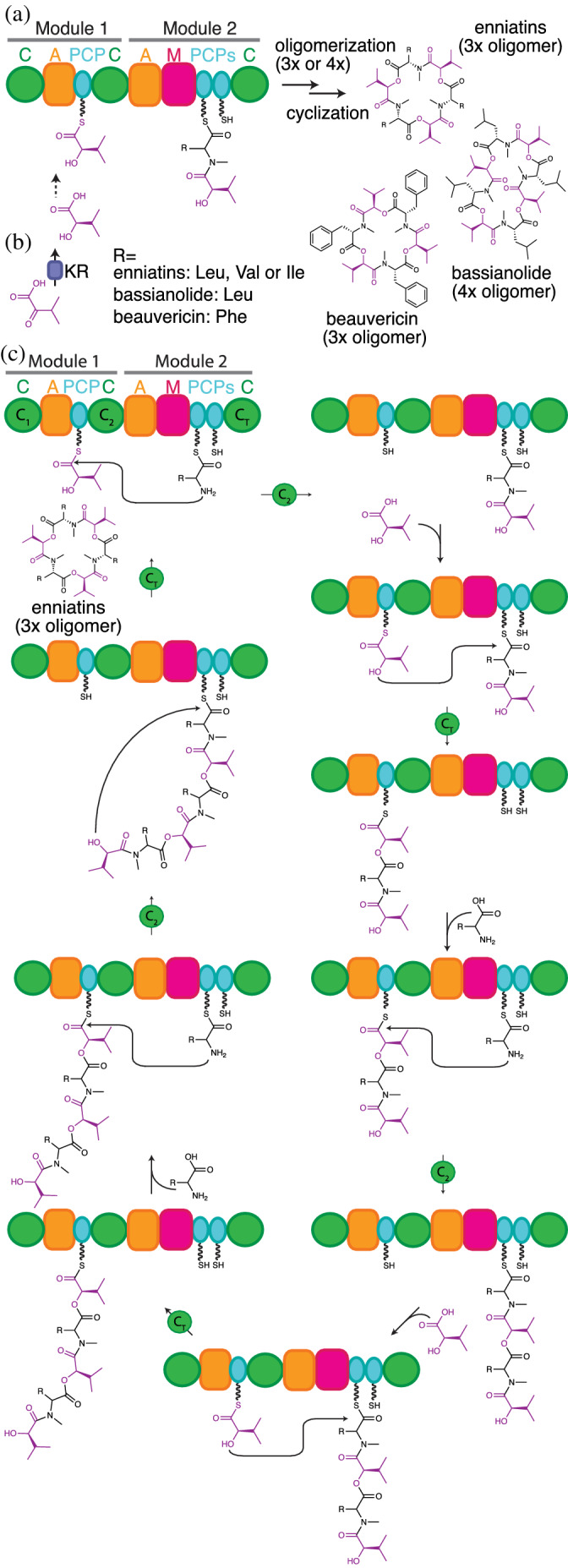
The proposed biosynthesis of enniatin, beauvericin and bassianolide. (a) Enniatin, bassianolide and beauvericin are made by di‐modular NRPSs. The C1 domain is inactive, and the adjacent PCP2a and PCP2b domains have redundant functions (b) Free‐standing ketoreductases (KR), unrelated to PKS KRs, generate α‐hydroxy acids from α‐keto acids. (c) Chain expansion proceeds through alternating condensation reactions catalyzed by the C2 (amide forming) and CT (ester forming) domains, where all PCP domains can alternate between donor or acceptor roles depending on the context of the catalyzed reaction and the nature of the attached substrate. Amino acid acceptor monomers are attached to PCP2a/b during C2 amide bond formation with elongated intermediate donors attached to PCP1, while hydroxy acid acceptor monomers are always attached to PCP1 in CT‐mediated ester bond formation with elongated intermediate donors attached to PCP2a/b. When the elongated chain reaches a specific length, the CT domain switches from elongation to cyclization activity through a yet unknown switching mechanism
