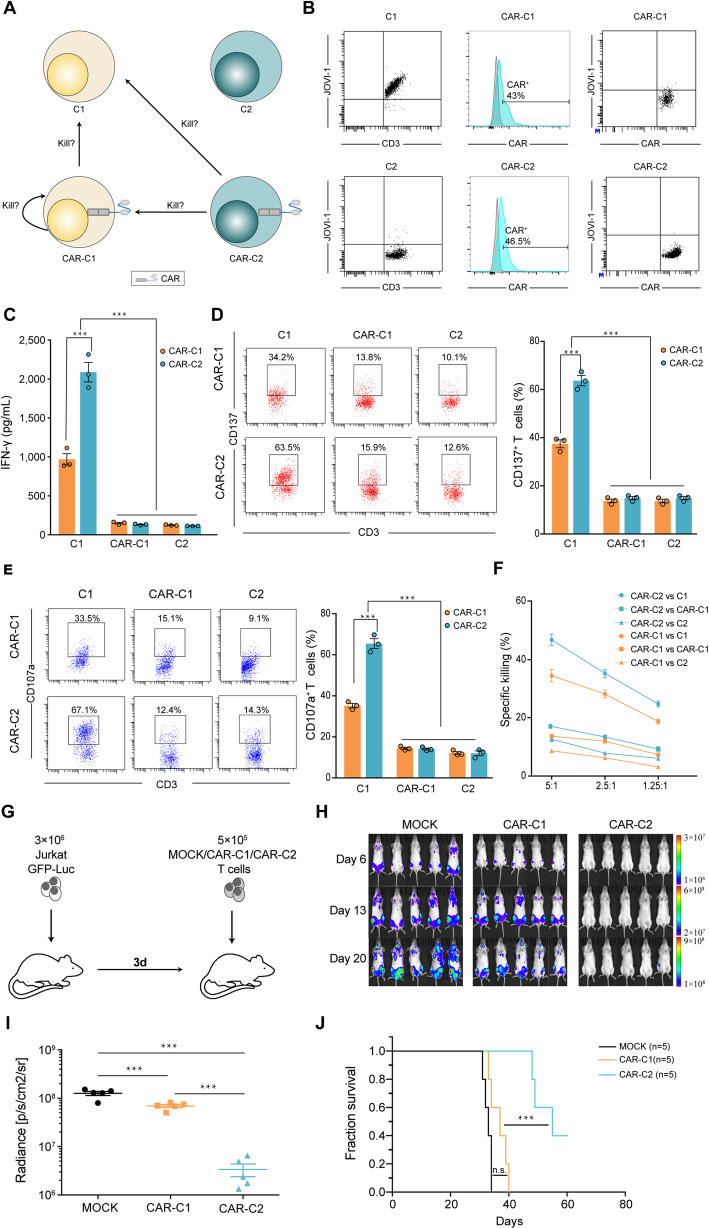
Fig. 1.
Effector functions of TRBC1+ and TRBC2+ cells genetically engineered with anti-TRBC1 CAR. a The categories and relationship of T cells following transduction with anti-TRBC1 CAR. TRBC1+ cells, C1; TRBC2+ cells, C2; anti-TRBC1 CAR transduced TRBC1+ cells, CAR-C1; anti-TRBC1 CAR transduced TRBC2+ cells, CAR-C2. b TRBC1 expression and CAR transduction efficacy of TRBC1-sorted and TRBC1-depleted T cells as well as CAR and TRBC1 expression of CAR-C1 and CAR-C2 analyzed by flow cytometry. c IFN-γ secretion by CAR-C1 and CAR-C2 against C1, CAR-C1 or C2 after 24-h co-culture. d-e Left, representive FACS profile of CD137 and C107a expression on CAR-C1 and CAR-C2 co-cultured with C1, CAR-C1 or C2. Right, percentages of CD137- and C107a-positive CAR-C1 and CAR-C2 following co-culture with C1, CAR-C1 or C2. f Cytotoxic activities of CAR-C1 and CAR-C2 against C1, CAR-C1 or C2 were examined by standard CFSE-based cytotoxity assays at several effector/target (E/T) ratios. g Scheme of the xenograft model. NOG mice (n = 5/group) were IV injected with 3 × 106 Luc/GFP–expressing Jurkat cells followed 3 days after by a single IV injection of 5 × 105 MOCK, CAR-C1 or CAR-C2. h IVIS imaging of tumor burden monitored by BLI at the indicated time points following MOCK, CAR-C1 or CAR-C2 T cell injection (day 0). i Radiance of individual mice at day 20 following MOCK, CAR-C1 or CAR-C2 T cell injection. n = 5 mice per group. j Kaplan-Meier survival curve of mice injected with mock, CAR-C1 or CAR-C2 T cells. ***P < 0.001 and n.s., not significant