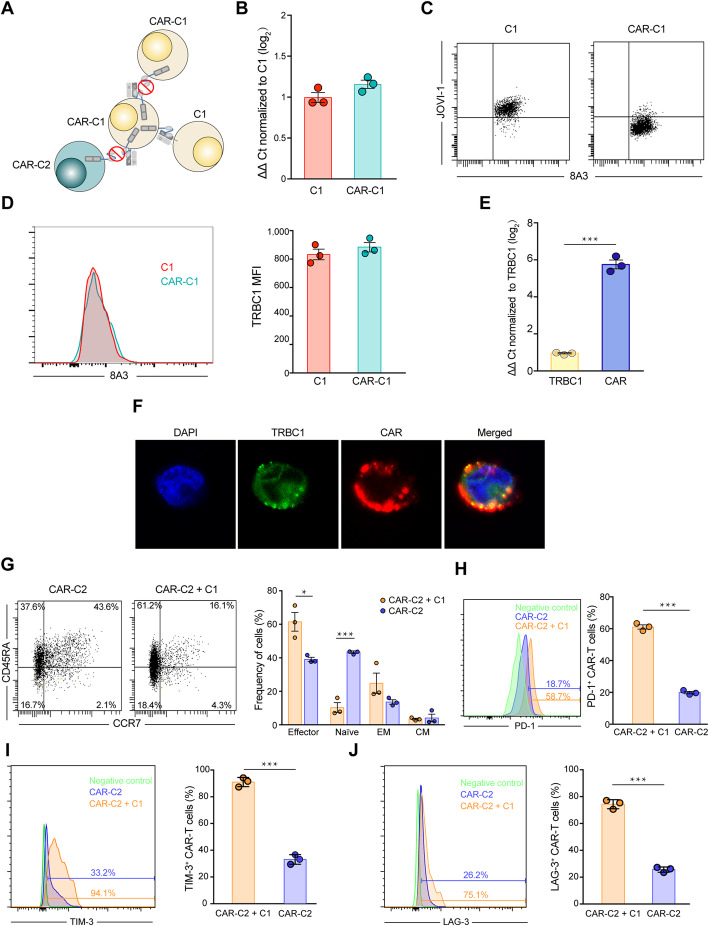
Fig. 2.
The cause for undetected TRBC1 and lesser effector function of CAR-C1. a Due to higher expression level of CAR than TRBC1 on CAR-C1, some CARs in cis bind to autologous TRBC1 on CAR-C1, resulting into masking TRBC1 from identification by other anti-TRBC1 CAR-T and meanwhile occupying these CARs, and thus only the remaining unoccupied CARs target TRBC1. b TRBC1 mRNA expression is maintained in CAR-C1 as compared to C1, as determined by qRT-PCR (ΔΔ Ct normalized to C1). c TRBC1 on C1 is detectable using both mAb 8A3 targeting TCRβ-chain constant region and mAb JOVI-1 from which the anti-TRBC1 CAR was derived, but TRBC1 on CAR-C1 cells is only recognized by mAb 8A3. d Left, representive FACS profile of TRBC1 expression on CAR-C1 and C1. Right, MFI of TRBC1 on CAR-C1 and C1. e Expression level of CAR was significantly higher than TRBC1 on CAR-C1 determined by qRT-PCR analysis (ΔΔ Ct normalized to TRBC1). f Confocal imaging of CAR-C1 using FITC-conjugated anti-TRBC1 antibody (green), TRITIK-conjugated anti-FLAG antibody (red), and DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 5 μm. g Left, representive FACS profile of CD45RA and CCR7 expression on CAR-C2 after 6-day culture alone or co-culture with C1. Right, percentages of naïve (CD45RA+ CCR7+), effector (CD45RA+ CCR7−), effector memory (CD45RA− CCR7−) and central memory (CD45RA− CCR7+) CAR-C2 cells. h-j Left, representive FACS profile of PD-1 (h), TIM-3 (i) and LAG-3 (j) expression on CAR-C2 after 6-day culture alone or co-culture with C1. Right, percentage of PD-1 (h), TIM-3 (i) and LAG-3 (j) positive CAR-C2. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001. Data are representative of three independent experiments