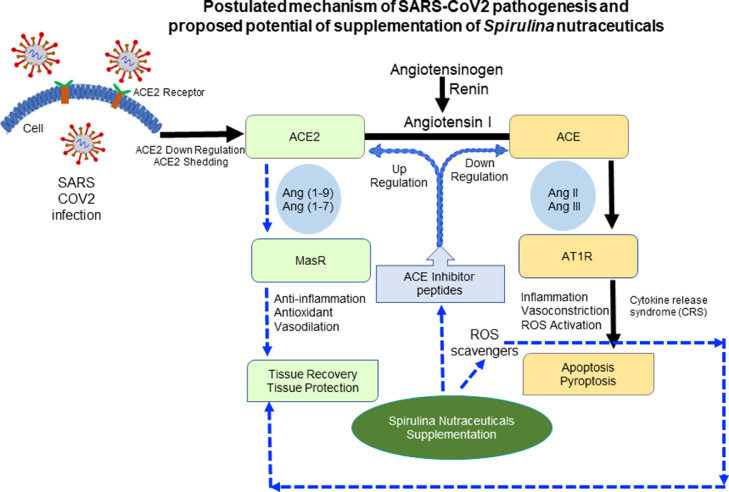
Fig. 1.
Postulated mechanism of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) 2 pathogenesis and proposed potential of supplementation of Spirulina nutraceuticals in alleviating oxidative stress and tissue injury. Similar to SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV2 is believed to infect host cells via binding of the virus spike protein with angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) 2 receptors of the host cell and lead to the downregulation of the ACE2. ACE2 is a suppressor of the renin-angiotensin system, where ACE catalyzes the conversion of angiotensin (Ang) I to Ang II, which further binds to angiotensin II type 1 receptors and induces acute tissue injury. On the other hand, ACE2 hydrolyzes Ang II to Ang 1 to 7 peptide that acts on the Mas receptor and protect from tissue injury. Supplementation of Spirulina nutraceuticals in SARS-CoV2 infection may help upregulate ACE2 activity and downregulate ACE activity that may further assist to overcome cytokine release syndrome and aid in tissue protection and repair.