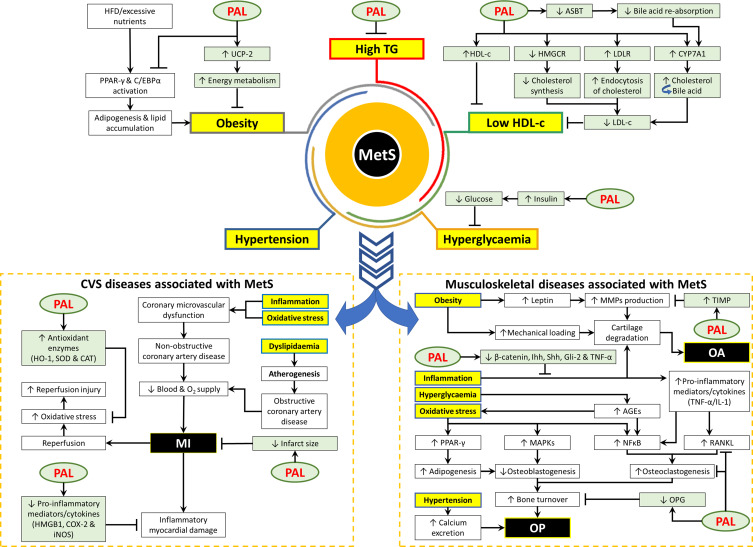
Figure 1.
The protective effects of palmatine on MetS and the associated diseases.
Abbreviations: ↓, decrease or downregulate; ↑, increase or upregulate; ┬, inhibit or suppress; AGEs, advanced glycosylation end products; ASBT, apical sodium-dependent bile acid transporter; CAT, catalase; COX, cyclooxygenase; C/EBP-α, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-α; HDL-c, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HFD, high fat diet; HMGB1, high mobility group box 1; HMGCR, 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl coenzyme A reductase; HO-1, heme oxygenase −1; iNOS, inducible NO synthase; Ihh, Indian hedgehog; LDL-c, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDLR, low-density lipoprotein receptor; MAPKs, mitogen-activated protein kinases; MI, myocardial infarction; MMP, matrix metalloproteinases; NFκB, nuclear factor kappa B; O2, oxygen; OA, osteoarthritis; OP, osteoporosis; OPG, osteoprotegerin; PAL, palmatine; PPAR-γ, proliferator-activated receptor-γ; RANKL, receptor activator of nuclear factor-kB ligand; Shh, Sonic hedgehog; SOD, superoxide dismutase; TG, triglyceride; TIMP-1, tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases 1; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; UCP-2, uncoupling protein-2.