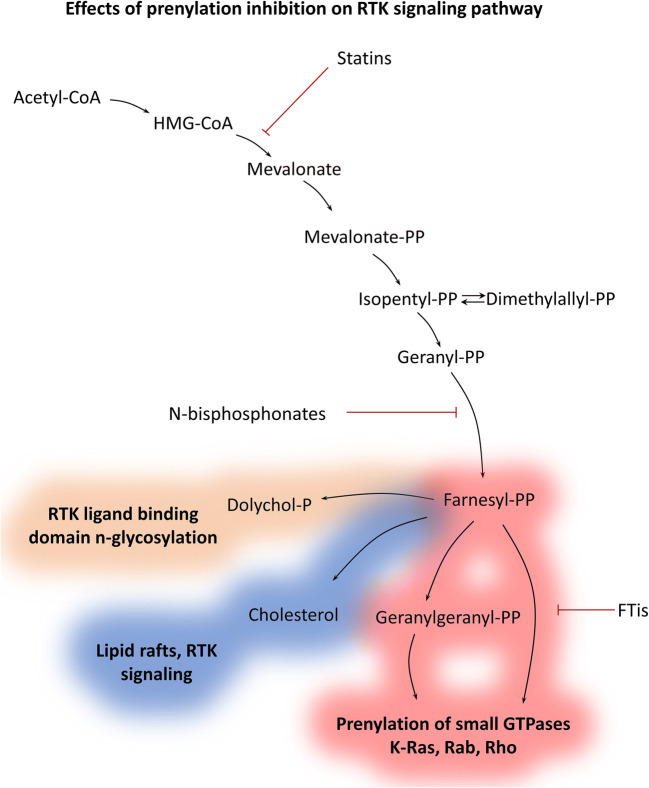
Fig. 2.
Effect of prenylation inhibition on receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) pathway. Distinct classes of prenylation inhibitors act on different levels of the mevalonate pathway. Statins and N-bisphosphonates shut down farnesyl-PP synthesis, leading to—besides inhibition of prenylation—depletion of dolichols and cholesterol. Dolichols are involved in N-glycolysation that is essential for proper ligand binding of certain RTKs, like EGFR. Cholesterol is a major compound of lipid rafts, specific microdomains of the plasma membrane functioning as signalization hubs in many major signaling pathways (e.g., EGFR and HER2). Prenylation inhibition concerns many major cellular process, like proliferation, survival, migration (K-Ras, Rheb Rho), vesicular transport, and autophagy (Rab). Interference with this metabolic pathway likely leads to pleiotropic effects