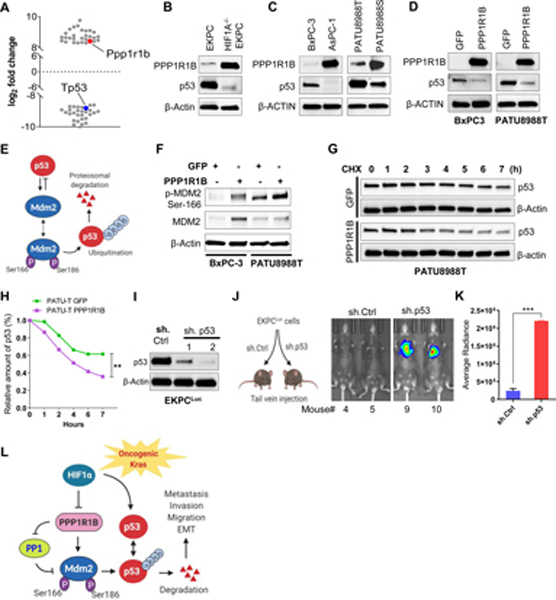
Figure 5: PPP1R1B promotes metastasis in pancreatic cancer by reducing p53.
(A) Scatter plot depicting the most significantly up or down regulated proteins (> ± log28) in HIF1A−/−EKPC cells compared with the EKPC cells. Proteins were organized by log2 fold change (Y-axis). PPP1R1B and p53 are indicated by red and blue respectively. (B,C) Immunoblot analysis of PPP1R1B and p53 levels in mouse and human pancreatic cancer cell lines. β ACTIN was used as control. (D) Western blot analysis of ectopic expression of PPP1R1B and its effect on p53 level in BxPC-3 and PATU8988T cells. GFP was used as control. (E) Schematic model of MDM2 and p53 feedback regulatory loop (F) Western blot analysis of phospho-MDM2Ser186, total MDM2 and β ACTIN in BxPC-3 and PATU-8988T cells overexpressing PPP1R1B. GFP was used as control. (G & H) Cycloheximide chase assay and quantification for p53 in PATU8988T cells overexpressing PPP1R1B or GFP. β-ACTIN was used as a loading control. (I) Western blot analysis of p53 and β ACTIN levels in EKPCLuc cells stably transfected with sh.Ctrl and two independent sh.p53. (J & K) Lung colonization of EKPCLuc + sh.p53 or EKPCLuc + sh.Ctrl cells bioluminescence imaging. N=5 for each group. ***p<0.0005 by t test (L) Schematic of the mechanistic link between loss of HIF1A, increased expression of PPP1R1B and degradation of the p53 protein that promotes invasion and metastasis in PDAC.