Figure 4.
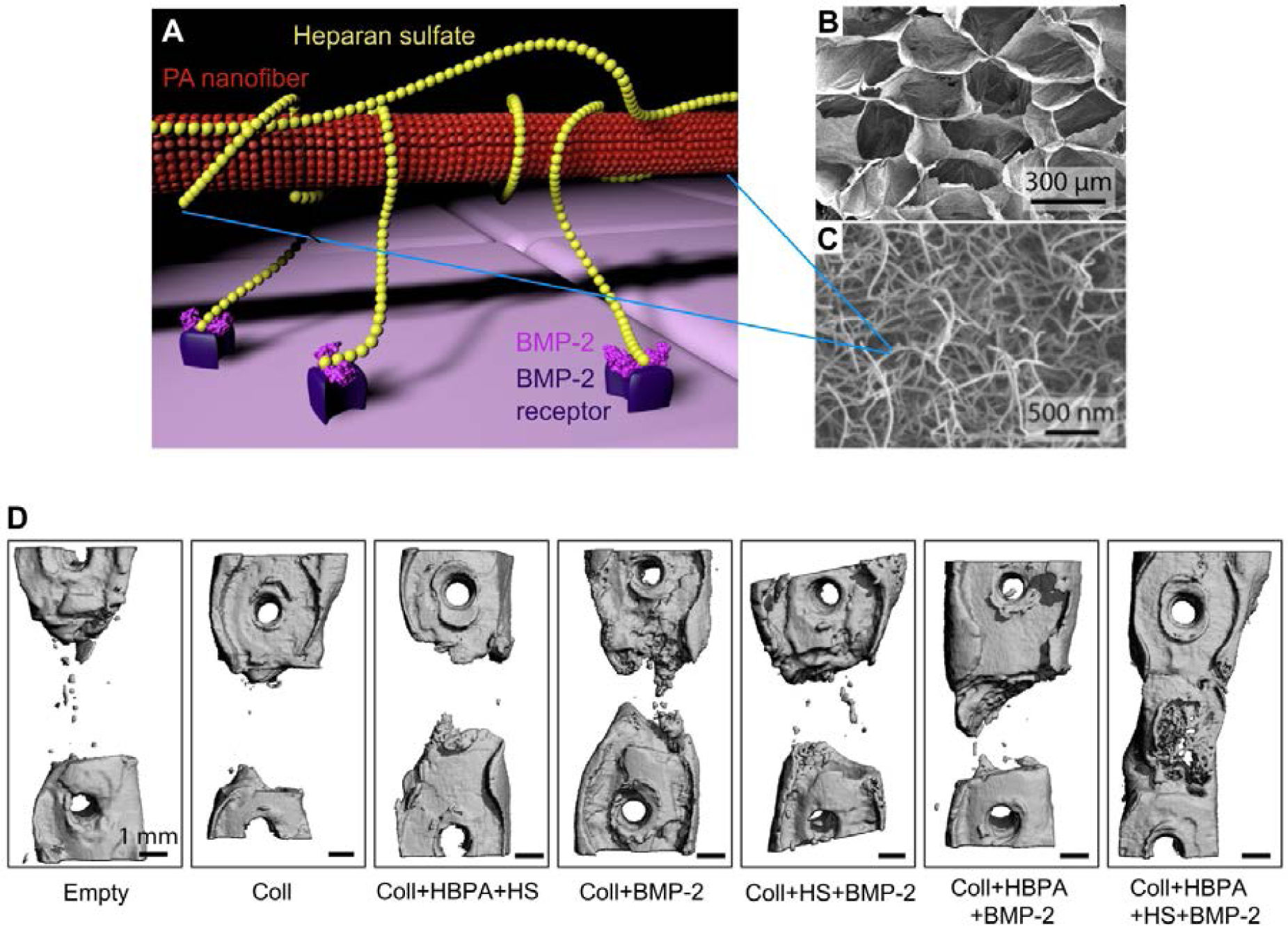
(A) Molecular graphics representation of heparin-binding PA structure and function. The heparin-binding PA nanofiber binds heparan sulfate, which is a lengthy polysaccharide. The heparan sulfate in turn binds BMP-2 growth factor and presents it to receptors on the cell membrane, thus potentiating the signal of BMP-2. (B) Empty porous collagen sponge, which heparin-binding PA nanofibers were loaded onto to improve surgical handling properties. (C) Scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of heparin-binding PA nanofibers, mixed with heparan sulfate and loaded onto a porous collagen sponge. (D) Representative microCT (computerized tomography) reconstructions of rat femur defects, showing the degree of bone healing after 6 weeks when treated with the indicated materials. Abbreviations: Coll – collagen sponge; HBPA – heparin-binding PA; HS – heparan sulfate. A) Adapted B-D) Reproduced with permission.163 Copyright 2013, Elsevier.
