Figure 5.
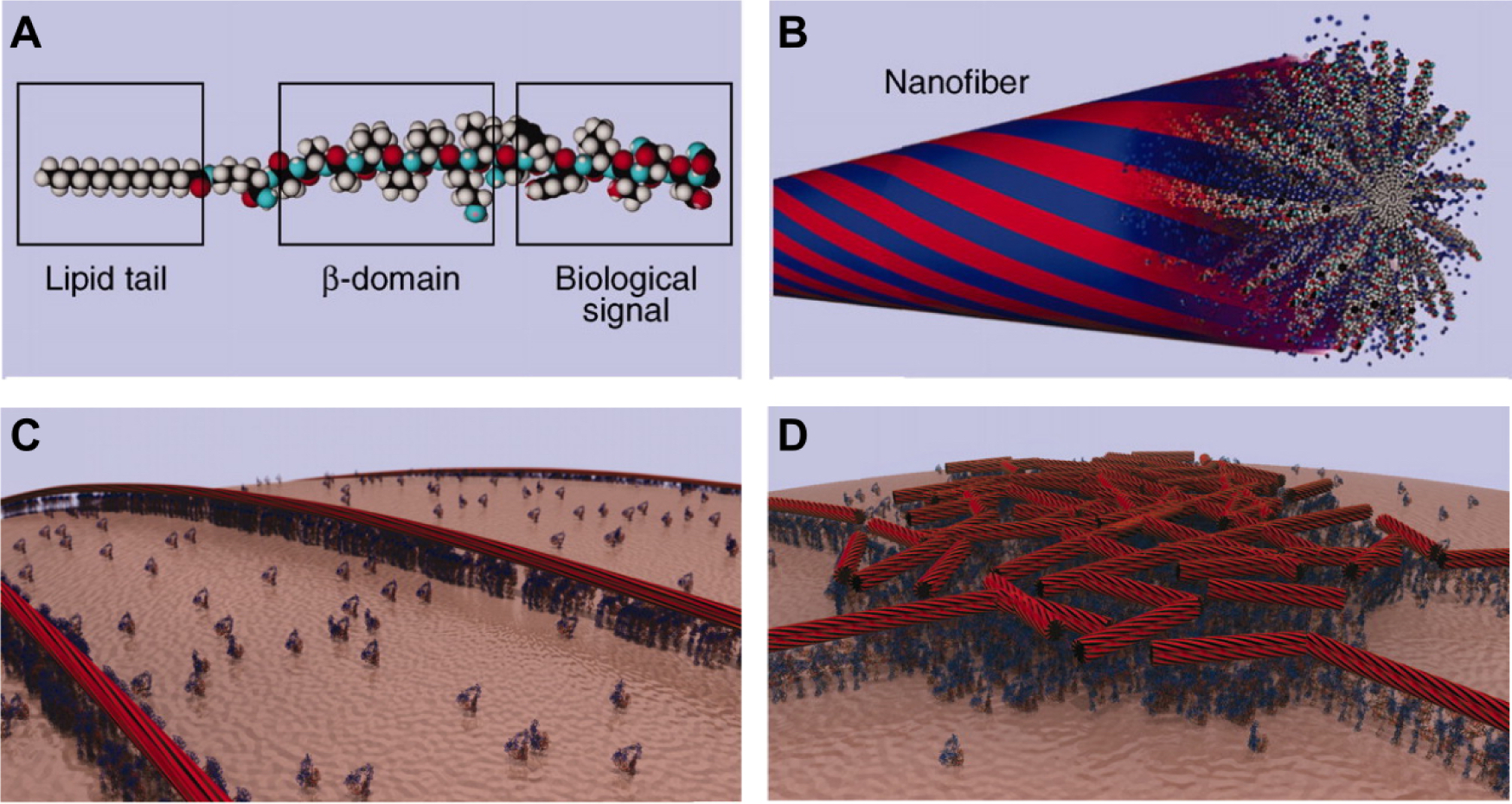
Molecular graphics representations showing (A) a PA molecule incorporating a bioactive peptide epitope and (B) the supramolecular nanofiber formed by these PA molecules. Due to hydrophobic collapse of the lipid tail in aqueous environments, the bioactive signals are displayed at high density of the surface of the nanofiber (idealized in red portions). The blue portions represent idealized water domains. (C) Molecular graphics representation of PA nanofibers concentrating and presenting biological signals to cell membranes. (D) Due to their non-covalent nature, PA nanofibers may dynamically rearrange over time as they interact with cells. In this molecular graphics representation, PA nanofibers have concentrated around a lipid raft structure where cell signaling activity is centered. Reproduced with permission.146 Copyright 2012, AAAS.
