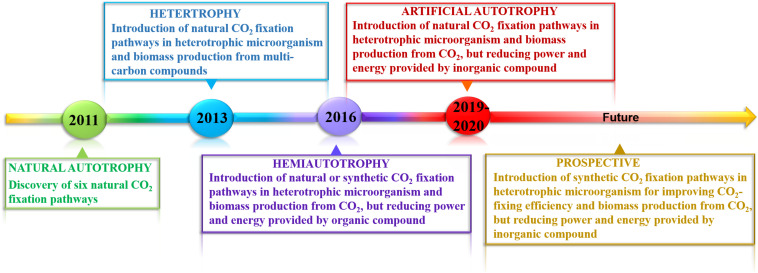
FIGURE 1.
Milestone in developing artificial autotrophy in the last decade. Until 2011, six naturally occurring CO2 fixation pathways have been identified, some of which were introduced into heterotrophic microorganisms. However, all of biomass was derived from additional multi-carbon compounds, such as glucose. The strong advances in synthetic biology enable the engineering of synthetic CO2 fixation pathways for improving carbon assimilation efficiency. Since 2016, hemiautotrophy has been successfully constructed by integrating natural or synthetic CO2 fixation pathways in heterotrophic hosts using organic compound as reducing power and energy source, in which biomass was completely derived from CO2. In 2019 and 2020, the conversion of heterotrophy to fully autotrophy was realized though integration of natural CO2 fixation pathways to support cell growth and inorganic compound’s oxidation to provide reducing power and energy.