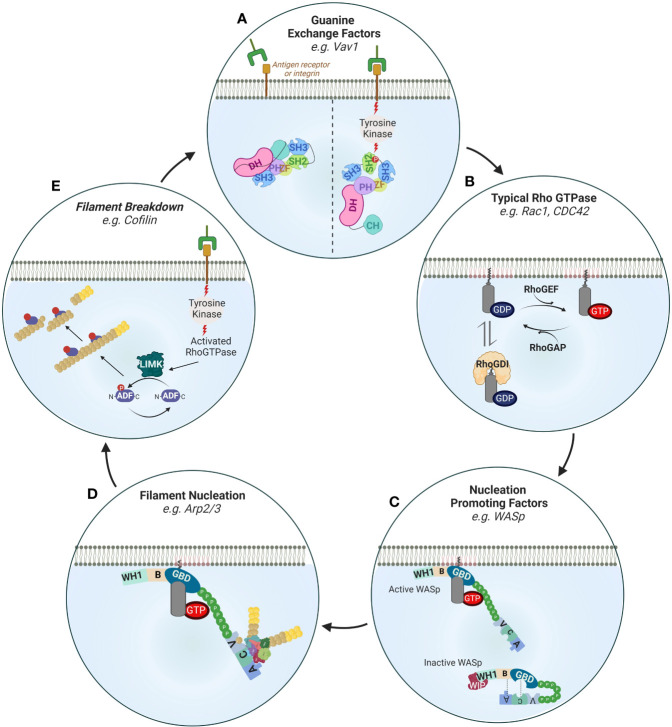
Figure 5.
Regulation of actin filament turnover. (A) Guanine exchange factors such as Vav1 are activated downstream of receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) signaling. Upon phosphorylation of its SH2 domain, Vav1 undergoes intramolecular reorganization that releases its nucleotide exchanging Dbl homology (DH)-pleckstrin homology (PH). Other important GEFs in immune cells are the DOCK family members (not shown). DOCKs are structurally different from the Vav family members in important ways. Namely, they contain lipid-binding domains (and thus are directly recruited to membranes) and lack DH-PH domains requiring association with the Elmo family of proteins to exchange nucleotides. (B) The activity of typical Rho GTPases is regulated by 1) GTP cycling and 2) intracellular retention by Rho GDI proteins. Rho GEFs such as Vav1, DOCK2 or DOCK8 enhance the exchange of GDP to GTP while Rho GAPs switch off Rho GTPases by enhancing the exchange of GTP with GDP. An important mechanism of signaling specificity is the preference of certain GEFs for certain Rho GTPases e.g. DOCK-2 to Rac, Gef-1 to CDC42 (not shown). (C) Nucleation promoting factors such as WASp are activated by Rho GTPases by relieving intramolecular folding (shown) or as in the case of the NPF WAVE regulatory complex by stabilizing a specific orientation (not shown). Inactive WASp in the cytoplasm is autoinhibited through interactions of its Basic Region (BR) with the Acidic (A) domain as well as its GTPase binding domain (GBD) with the central (C) domain. Interaction with activated CDC42 (through the GBD) and recruitment to the plasma membrane (through PIP2) relieves this inhibited conformation. Through its WH1 domain WASp also interacts with WIP which regulates its activity. (D) Activated membrane-proximal WASp interacts with the Arp2/3 complex to mediate the nucleation of new filaments at a 70° angle by direct binding of its CA domains to Arp2/3 and to profilin and actin through its verprolin (V) domain. Other important actin nucleators are the formins that are also similarly activated by relief of autoinhibitory intramolecular folding following interaction with Rho GTPases downstream of tyrosine kinase signaling (not shown). (E) Receptor tyrosine kinases also activate filament breakdown which is important in maintaining a pool of profilin actin monomers that can be used for de novo actin polymerization as well as feedback regulation of activation. A key protein in actin severing is cofilin which enhances filament severing and breakdown by decorating actin filaments. Cofilin is activated by LIMK mediated phosphorylation.