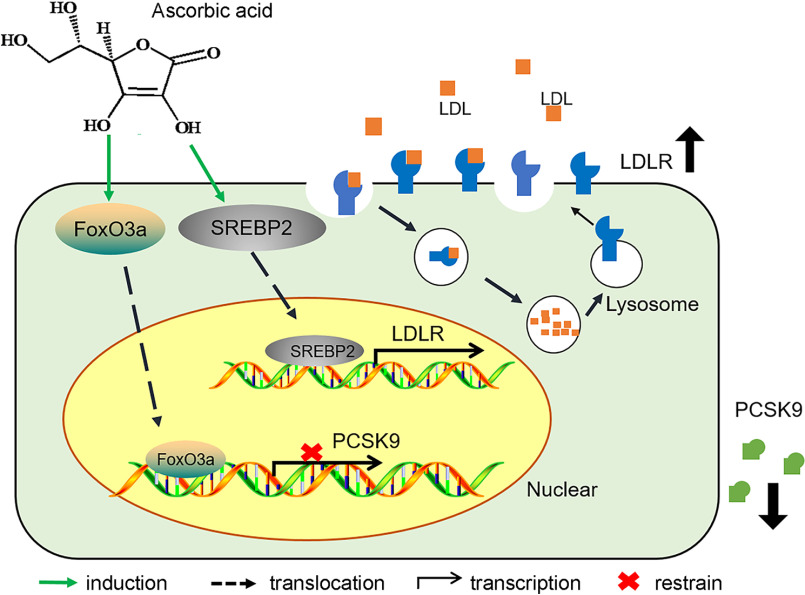
Figure 7.
Identifying the role of ascorbic acid in regulating PCSK9-LDLR pathway. Treatment of hepatocytes or mice with ascorbic acid activates FoxO3a, which results in inhibition of PCSK9 transcription and activation of LDLR protein expression. In addition, ascorbic acid is able to activate the SREBP2 pathway, which leads to activation of LDLR transcription. These two pathways work together to enhance LDLR activity and ameliorate cholesterol metabolism, particularly in the species relying on exogenous ascorbic acid supplement.