Figure 7.
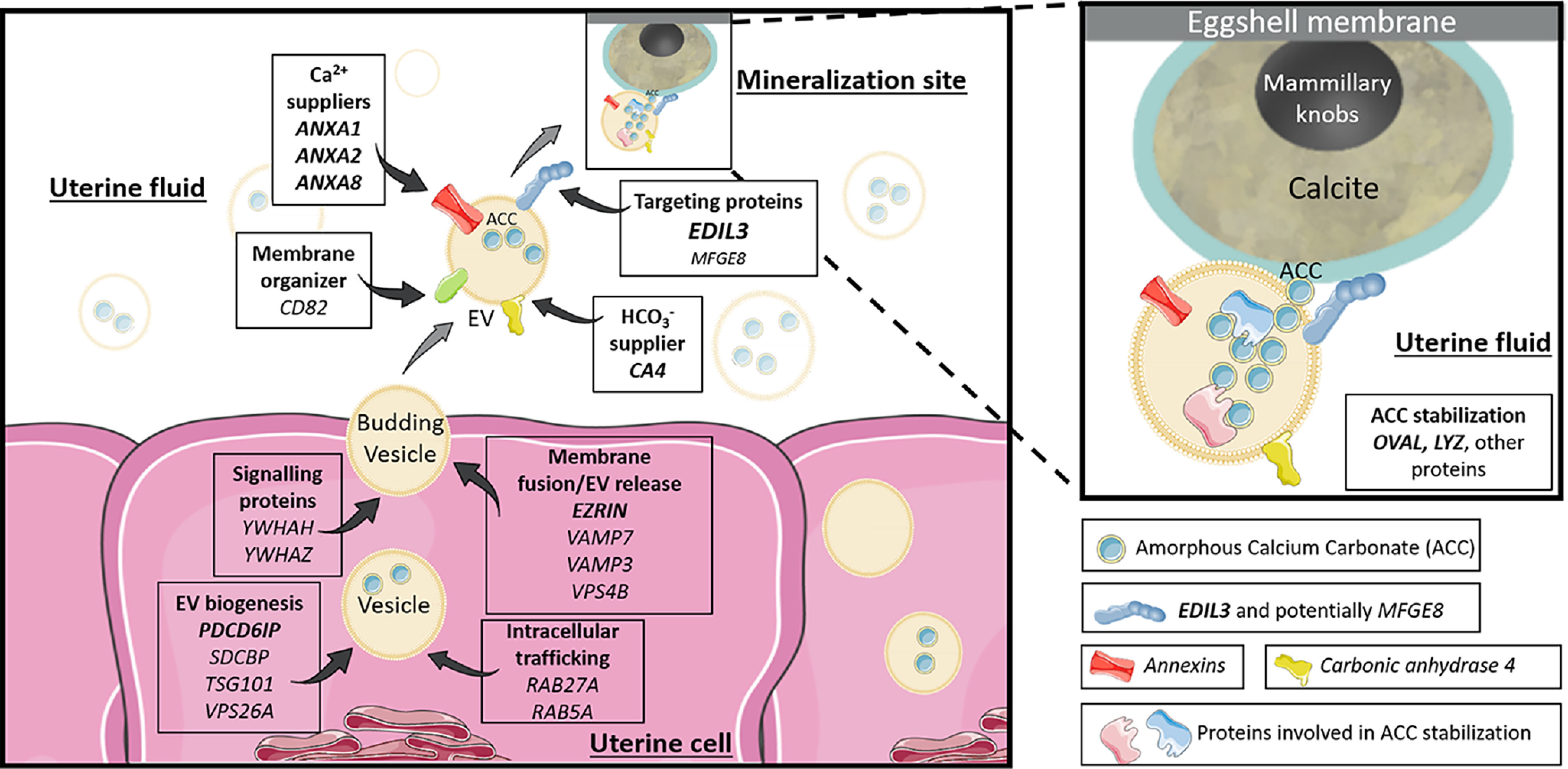
Proposed vesicular function for the different genes and proteins investigated in the study. The EVs bud by exocytosis from the plasma membrane of the uterine cells. ANXA1, -2, -8, and CA4 supply calcium and bicarbonate ions, respectively (inside uterine cells or in the UF). The EVs transit the UF to deliver stabilized ACC to the mineralization sites. The passage of EV-encapsulated ACC avoids nonspecific precipitation in the UF and provides stabilized ACC to the mineralization sites. OVA and LYZ stabilize ACC inside vesicles. EDIL3 (in bold), and to a lesser extent MFGE8, guide the EVs by targeting calcium to the mineralization front. The rest of the proteins are involved in EV biology (biogenesis, intracellular transport, and release). The genes in bold represent proteins identified in our proteomic and/or immunofluorescence analyses. Elements were from Servier Medical Art (https://smart.servier.com/), licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License.
