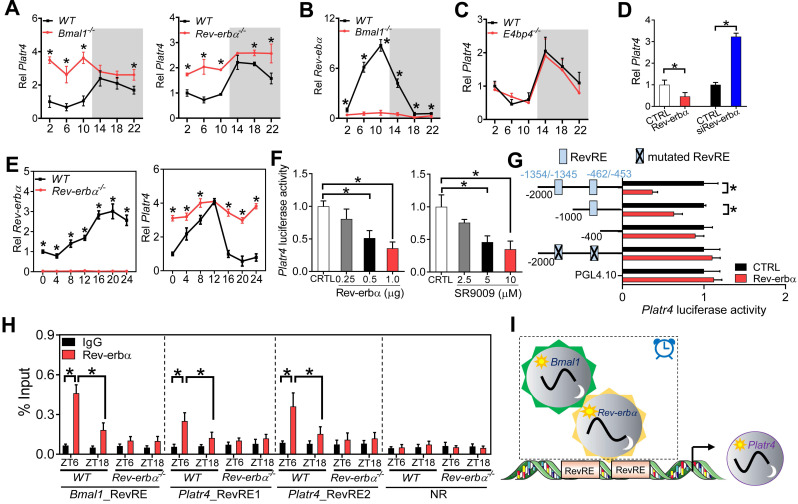
Figure 2.
Rev-erbα regulates rhythmic expression of Platr4 in normal mice. (A) Hepatic Platr4 expression in the Rev-erbα-/-, Bmal1-/- and wild-type (WT) mice at 6 circadian time points. Data are mean ± SD (n = 5). *p <0.05 versus WT at individual time points (two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test). (B) Hepatic Rev-erbα expression in the Bmal1-/- and WT mice at 6 circadian time points. Data are mean ± SD (n = 5). *p <0.05 versus WT at individual time points (two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test). (C) Platr4 expression in the livers of E4bp4-/- and WT mice at 6 circadian time points. Data are mean ± SD (n = 5). (D) Effects of Rev-erbα overexpression and knockdown on Platr4 expression in BMDMs. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3). *p <0.05 (t-test). (E) Temporal expression of Rev-erbα (left panel) and Platr4 (right panel) in synchronized BMDMs derived from Rev-erbα-/- and WT mice. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3). *p <0.05 versus WT at individual time points (two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test). (F) Effects of Rev-erbα overexpression (left panel) and SR9009 (a Rev-erbα agonist, right panel) on the 2.1-kb Platr4 promoter activity in BMDMs. Data are mean ± SD (n = 6). *p <0.05 (one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test). (G) Effects of Rev-erbα on the activities of different versions of Platr4-Luc reporters. Data are mean ± SD (n = 6). *p <0.05 (t-test). (H) Recruitment of Rev-erbα protein to the two RevRE sites (-1354/-1345 and -462/-453 bp) of Platr4 promoter in livers derived from WT and Rev-erbα-/- mice at ZT6 and ZT18. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3). *p <0.05 (two-way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test). (I) Schematic diagram showing the potential mechanism for rhythmic expression of Platr4. NR, non-binding region.