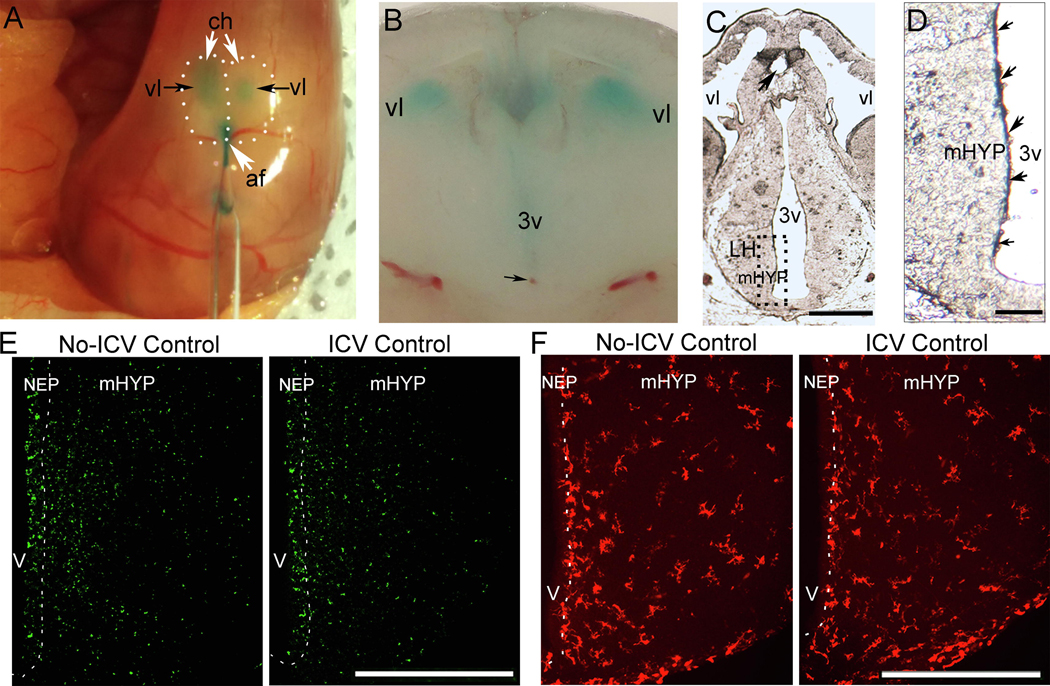
Figure 2:
A dye solution (0.1% Fast Green in normal saline) was used and histological analyses were performed to investigate the ICV injection technique, verify the injection site, and determine the nature and extent of spread of the injected solution. Immunofluorescence histochemistry (IF) was also performed to examine the effects of the injection procedure on cells in the NEP and LH. A, Photomicrograph of surface of embryo brain illustrates the dye solution injected through the anterior fissure as it fills the lateral ventricles of an E16 embryo. B, Coronal brain slice shows dense concentration of dye solution in the third ventricle and the tip of injection site (black arrow) in the ventral region. C, Cryostat-cut section from E14 brain shows point of entry of injector (black arrow) in the third ventricle. D, Higher magnification shows dense concentration of the dye solution within the NEP, indicated by blue and purple colored spots (small black arrows) along the third ventricle. E, Photomicrographs of ICV Control compared to No-ICV Control groups stained with TUNEL, a marker for apoptosis, show ICV injection of dye solution has no effect on TUNEL+ cells in the NEP and LH of E19 embryos (data in Table 4). F, Photomicrographs of ICV Control compared to No-ICV Control groups stained with Iba-1, marker for microglia, show ICV injection of dye solution has no effect on the density of Iba-1+ cells in the NEP and LH of E19 embryos (data in Table 4). Abbreviations: af: anterior fissure; ch, cortical hemisphere; IF, immunofluorescence; mHYP, medial hypothalamus; NEP, neuroepithelium; 3v, third ventricle; vl, lateral ventricle; Scale bars, 500 μm.