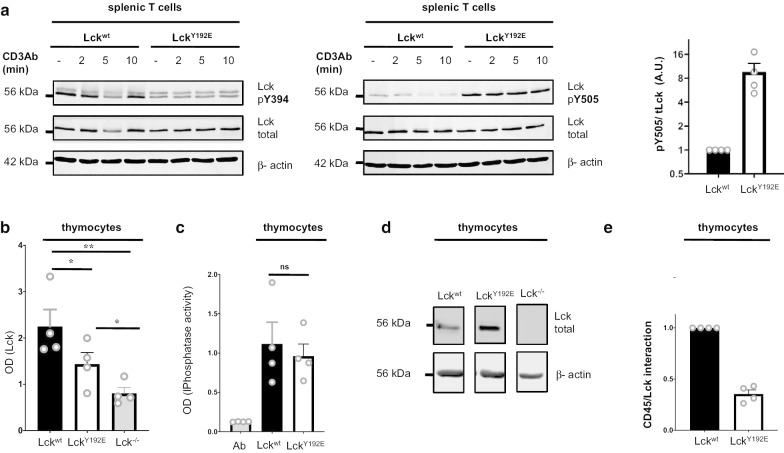
Fig. 4.
Hyperphosphorylation of Y505 in LckY192E and decreased LckY192E/CD45 interaction. a Splenic T cells from Lckwt and LckY192E knock-in mice were stimulated for the indicated periods of time. Cells were subsequently lysed and the phosphorylation of Y394 and Y505 assessed using phosphospecific antibodies. The bar graph (right) shows the quantification of Lck phosphoryation on Y505 from four independent experiments. b Murine thymocytes were lysed and CD45 was immunoprecipitated in a 96-well plate. CD45-associated Lck was detected using an Lck antibody and a secondary alkaline phosphatase-conjugated Ab in a Tecan plate-reader. Thymocytes from Lck−/− mice were used as negative control. c The amount of CD45 immunoprecipitated in b was assessed using a phosphatase assay. Ab represents the antibody control. d The amount of Lck in the input lysates used in b was assessed using an immunoblot. e Data in b were normalized against Lck expression shown in d to quantify CD45/Lck association. Each dot represents one experiment (n = 4). Statistical analyses were performed using a paired Student’s t test, **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05, ns not statistically significant