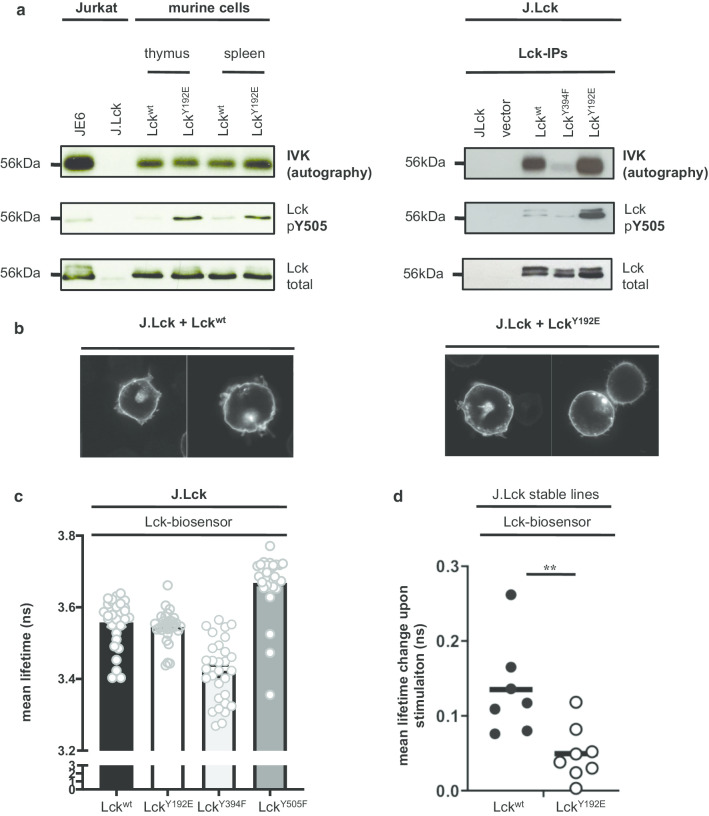
Fig. 5.
LckY192E is catalytically active and in a conformation like Lckwt. a Thymocytes and splenic T cells from Lckwt and LckY192E knock-in mice (left) or J.Lck cells reconstituted with the indicated Lck constructs (right) were lysed and Lck was immunoprecipitated. Immunoprecipitaes were incubated with [32P] ATP and proteins were subsequently separated by SDS-PAGE. The activity of Lck was monitored by autoradiography, whereas the expression of Lck and the phosphorylation levels of Y505 were analyzed by immunoblotting. Lck immunoprecipitates from JE6 and J.Lck in the left panel were use as positive and negative control, respectively. Catalytically inactive LckY394F in the right panel was used as negative control. One representative of two independent experiments is shown. b J.Lck expressing either Lckwt or LckY192E were labeled with an Lck antibody. Pictures were taken using a confocal microscope. The left panel show the subcellular localization of Lckwt, while the right panel covers LckY192E. c Lck-deficient J.Lck T cells were reconstituted with the indicated Lck-biosensor constructs. Graphs show mean lifetime of FLIM/FRET analyses. The constitutively closed (Y394F) and constitutively open (Y505F) Lck mutants served as controls as reported previously [18, 20, 21]. Dots represent individual cells from 3 experiments and the arithmetic mean ± SEM was calculated. d Lck-deficient Jurkat cells (J.Lck) stably expressing either a LckWT biosensor or a Lck biosensor carrying the Y192E mutation were used for dynamic FLIM/FRET measurements as previously described [18, 21]. Change in mean lifetime upon CD3 stimulation was calculated from 7 to 8 cells from two independent experiments (n = 2). Horizontal bar represents the mean, which was 0.135 ns for LckWT and 0.049 ns for LckY192E. Each dot represents one cell. Statistical analyses were performed using an unpaired Student’s t test **p < 0.01