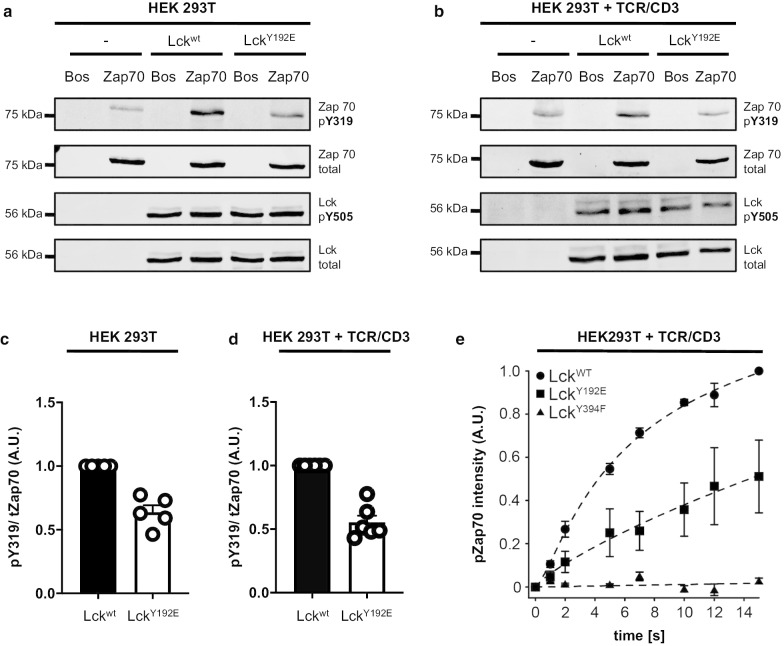
Fig. 6.
LckY192E displays an impaired ability to phosphorylate ZAP70 independently of Y505 phosphorylation. a HEK 293T cells (–) or HEK 293T cells stably expressing either Lckwt or LckY192E were transiently transfected with either an empty vector (Bos) or Myc-tagged ZAP70 (75 kDa). The phosphorylation of ZAP70 on Y319 (used as a read-out for Lck activity) as well as the phosphorylation of Lck on Y505 were monitored using phosphospecific antibodies. One representative experiment is shown (n = 5). b Parental TCR/CD3+ HEK 293T cells (–) or TCR/CD3+ HEK 293T cells stably expressing Lckwt, or LckY192E were transiently co-transfected with either a Myc-tagged ZAP70 or an empty vector (Bos). Subsequently, cells were lysed and the phosphorylation of pY319 of ZAP70 and pY505 of Lck were assessed using phosphospecific antibodies. One representative experiment is shown (n = 6). c, d The densiometric mean values of the phosphosignal pY319 in a and b were normalized against the value of the total ZAP70 signal. The bar graph shows the calculated mean + SEM values of the normalized ZAP70 phosphorylation in HEK 293T (c) and the TCR/CD3+ HEK 293T (d) cell systems. One dot represents one experiment. e Photo-caged Lck (WT, Y394F and Y192E) and ZAP70 were transiently transfected in TCR/CD3+ HEK 293T cells. Lck kinase activity was initiated by global illumination of the cells and the kinetics of ZAP70 phosphorylation by Lck was measured at defined time points by quantitative fluorescent Western blot analysis. Data were fit using a three-parameter logistic function and are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3)