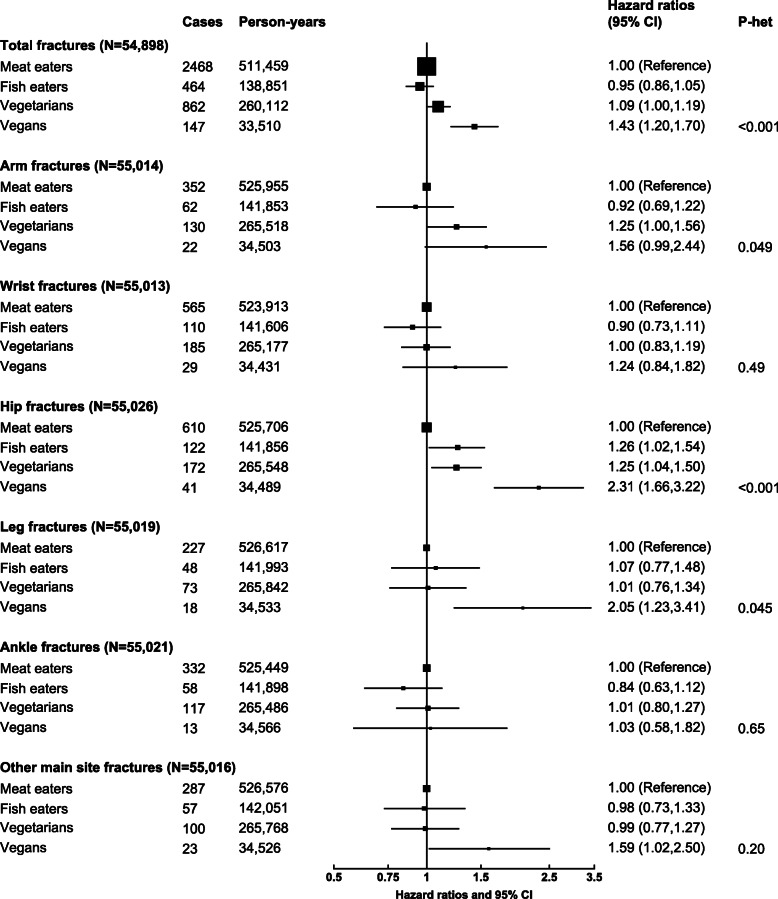
Fig. 1.
Risks of total and site-specific fractures by diet group in EPIC-Oxford. Estimates also shown in Table 2 as model 2. All analyses were stratified by sex, method of recruitment (general practice or postal), and region (7 categories), and adjusted for year of recruitment (per year from ≤ 1994 to ≥ 1999), ethnicity (white, other, unknown), Townsend deprivation index (quartiles, unknown), education level (no qualifications, basic secondary (e.g. O level), higher secondary (e.g. A level), degree, unknown), physical activity (inactive, low activity, moderately active, very active, unknown), smoking (never, former, light, heavy, unknown), alcohol consumption (< 1 g, 1–7 g, 8–15 g, 16+ g/day), dietary supplement use (no, yes, unknown), height (5 cm categories from < 155 to ≥ 185 cm, unknown), body mass index (< 18.5, 18.5–19.9, 20–22.4, 22.5–24.9, 25–27.4, 27.5–29.9, 30–32.4, ≥ 32.5 kg/m2, unknown), and in women menopausal status (premenopausal, perimenopausal, postmenopausal, unknown), hormone replacement therapy use (never, ever, unknown), and parity (none, 1–2, ≥ 3, unknown). Other main site fractures are defined as fractures of the clavicle, rib, or vertebra