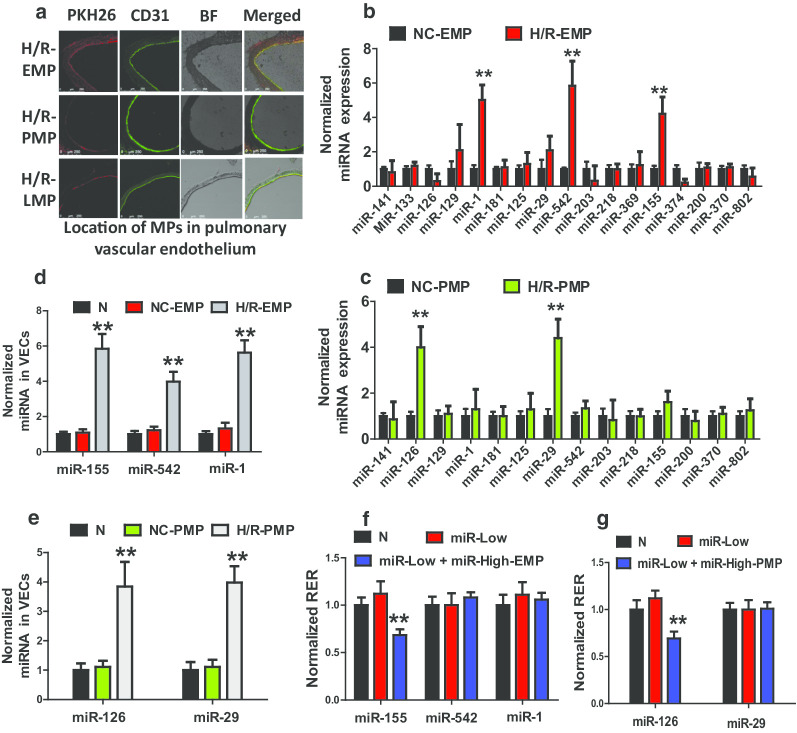
Fig. 3.
The role of miRNAs in EMPs and PMPs in pulmonary vascular leakage and lung injury. a The localization of H/R-LMPs, H/R-EMPs, and H/R-PMPs in the pulmonary vascular endothelial cells after intravenous administration. The vascular endothelial cell was stained with CD31 antibodies (green), and MPs were stained with PKH26 (red). b Level of miRNAs related to vascular permeability in NC-EMPs and H/R-EMPs. c The level of miRNAs related to vascular permeability in NC-PMPs and H/R-PMPs. d Level of miRNAs in VECs 1 h after NC-EMPs and H/R-EMPs treatment. e Level of miRNAs in VECs 1 h after NC-PMPs and H/R-PMPs treatment. f Effect of miRNAs transported by EMPs on the TER of monolayer VECs. g Effect of miRNAs transported by PMPs on the TER of monolayer VECs. Data are the mean ± SD of n experiments (n = 8). miR-Low: miRNA low expression; miR-High-EMP: miRNA-high containing EMP; miR-High-PMP: miRNA-high containing PMP. **P < 0.01 versus N groups or NC-EMP groups or NC-PMP groups