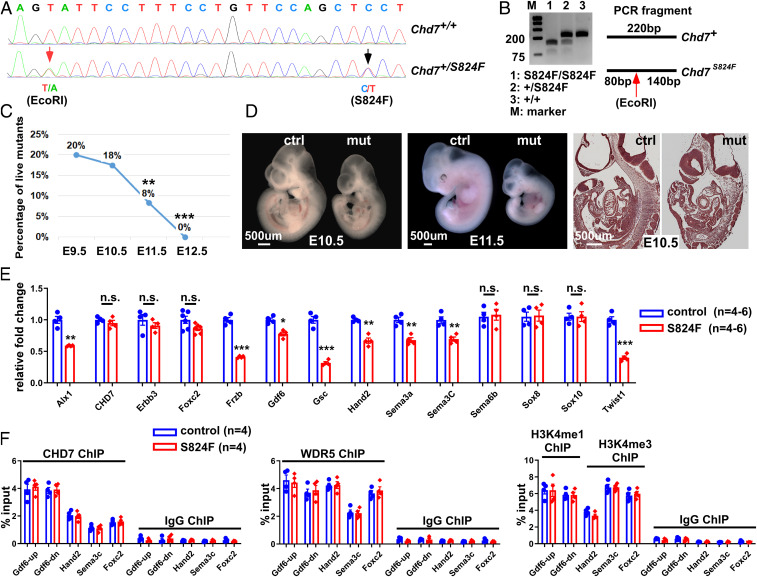
Fig. 6.
CHD7 regulates embryo development and target genes through ATP-dependent and -independent activities. (A) The S824F allele was knocked into the endogenous Chd7 locus through CRISPR/Cas9. Successful knockin was confirmed by genomic DNA sequencing of the founder mouse. The red arrow indicates a silent mutation that generates an EcoRI site (introduced to facilitate genotyping), while the black arrow indicates the C-to-T mutation that generates the S824F mutation. (B) PCR products from mice with different genotypes were digested with EcoRI. (C) Percentage of live mutant embryos (Chd7S824F/S824F) from the self-cross of Chd7S824F/+ mice. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, χ2 test. (D) Control (Ctrl, Chd7+/+) and mutant (mut, Chd7S824F/S824F) embryos at E10.5 (Left) and 11.5 (Center) were subjected to whole mount and section examination (Right). (E) Total RNA was isolated from GFP+ cells of the PA3–6 regions of control (Wnt1-Cre2;Chd7+/+;R26mtmg/+) and mutant (Wnt1-Cre2;Chd7S824F/S824F;R26mtmg/+) embryos (25 to 35 somites). qRT-PCR was performed to examine expression of the indicated genes. n.s., no significant difference; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test. (F) GFP+ cells were isolated from the PA3–6 regions of control (ctrl, Wnt1-Cre2;Chd7+/+;R26mtmg/+) and mutant (Wnt1-Cre2;Chd7S824f/S824F;R26mtmg/+) embryos followed by ChIP-qPCR using antibodies against CHD7, WDR5, H3K4me1 (for Gdf6up and Gdf6-dn), and H3K4me3 (for Hand2, Sema3C, and Foxc2), as indicated. A preimmune IgG was used as a control.