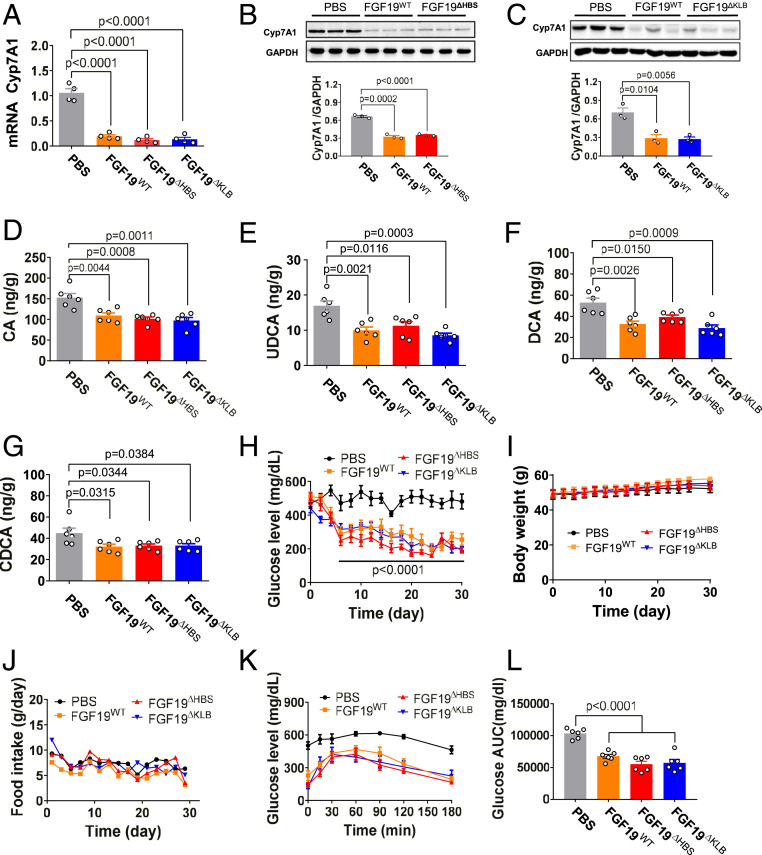
Fig. 3.
FGF19ΔHBS and FGF19ΔKLB have FGF19WT-like BA and glucose regulatory activities. C57BL/6J or db/db mice were injected with either FGF19WT or its variants (all at 21 nmol/kg of body weight), or with PBS as a control. (A) Real-time PCR analysis of Cyp7A1 mRNA levels in C57BL/6J liver extracts 4 h after injection. Data are presented as mean values ± SEM (n = 4); a value of P < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. (B and C) Protein expression (Upper) and quantification (Lower) of Cyp7A1 determined by Western blotting in extracts from livers of db/db mice after chronic administration for 1 mo. Data are presented as mean values ± SEM (n = 3); a value of P < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. (D–G) Tissue levels of CA (D), UDCA (E), DCA (F), and CDCA (G) in livers of db/db mice treated for 1 mo. Data are presented as mean values ± SEM (n = 6); a value of P < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. (H–J) Blood glucose (H), body weight (I), and food intake (J) in ad libitum-fed db/db mice after chronic daily treatment with FGF19WT, FGF19ΔHBS, or FGF19ΔKLB. (K and L) A GTT done after chronic treatment of db/db mice (K) and the accompanying integrated AUC (L) for changes in blood glucose. Data are presented as mean values ± SEM (n = 6); a value of P < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.