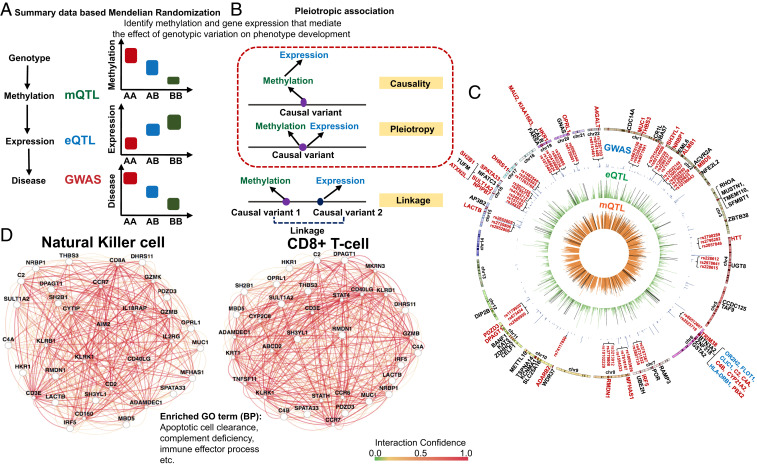
Fig. 5.
SMR to define genetic variations driving methylation and gene-expression changes. (A) We used SMR to distinguish scenarios, where the effect of a genetic variant on transcription is mediated by methylation. (B) Pleiotropic association test was conducted to distinguish causality, pleiotropy, and linkage. Causality: The effect of a genetic variant on transcription is mediated by methylation. Pleiotropy: A genetic variant has direct effects on both methylation and transcription. Linkage: Genetic variants in LD affecting methylation and transcription independently. (C) The moloc and SMR results are shown on a Circos plot. Negative log10 of P value of inner (orange ring) mQTL (blood), middle (green ring) eQTL [blood; GTEx V7 (53)], and GWAS (blue ring) (28). Only the lead SNP for each mCpG or eGene, and significant GWAS SNPs (two-sided PEWAS < 5E-08) were plotted. Significant moloc regions that covered 1,142 eGFR significant GWAS variants and 267 CpG sites were highlighted by the black lines in the green ring and orange ring, respectively. Eighty-five genes were highlighted in dark red color and bars on the outmost chromosomes ring. Seventy-one protein-coding genes were labeled with their gene names. Nine protein-coding genes located within MHC regions were highlighted in blue color. Gene names of the 31 high fidelity CKD risk genes and 2 to 3 representative SNPs in the center of regions showing significant pleiotropic associations were highlighted in dark red. (D) Pathway analysis performed by GIANT (51), indicating that high-fidelity CKD causal genes were enriched for immune function, including apoptotic cell clearance, and also strongly coexpressed in NK cells and CD8+ cells.