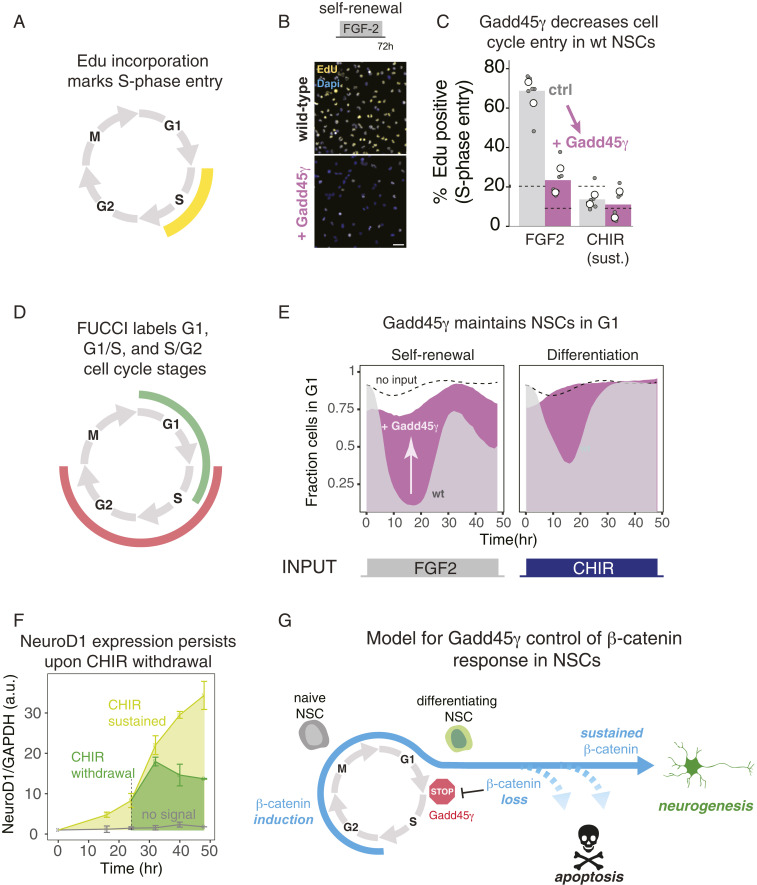
Fig. 5.
Gadd45γ blocks cell-cycle progression in NSCs. (A) Edu incorporation occurs during DNA synthesis in S phase. (B) Ectopic Gadd45γ expression blocks Edu incorporation and cell-cycle entry in NSCs under both self-renewal conditions (20 ng/mL FGF2) and neurogenic conditions (3 μM CHIR) (B and C). Data in C represent the means of two experiments (white circles), each of which was performed with biological triplicates (gray circles). (Scale bar, 100 μm.) (D) FUCCI reporters are fluorescent indicators that mark a cell’s position in the cell cycle. (E) Live-cell imaging of the FUCCI system in NSCs shows that ectopic Gadd45γ expression blocks cell-cycle entry in response to both self-renewal and neurogenic stimuli. (F) β-Catenin–dependent expression of the early neurogenic factor NeuroD1 persists in NSCs despite withdrawal of the β-catenin stimulus. Data represent quantitation of Western blots (mean ± 1 SE of biological duplicates, see SI Appendix, Fig. S12). (G) Model for how Gadd45γ regulates differential cell-fate control downstream of β-catenin dynamics.