Fig. 3.
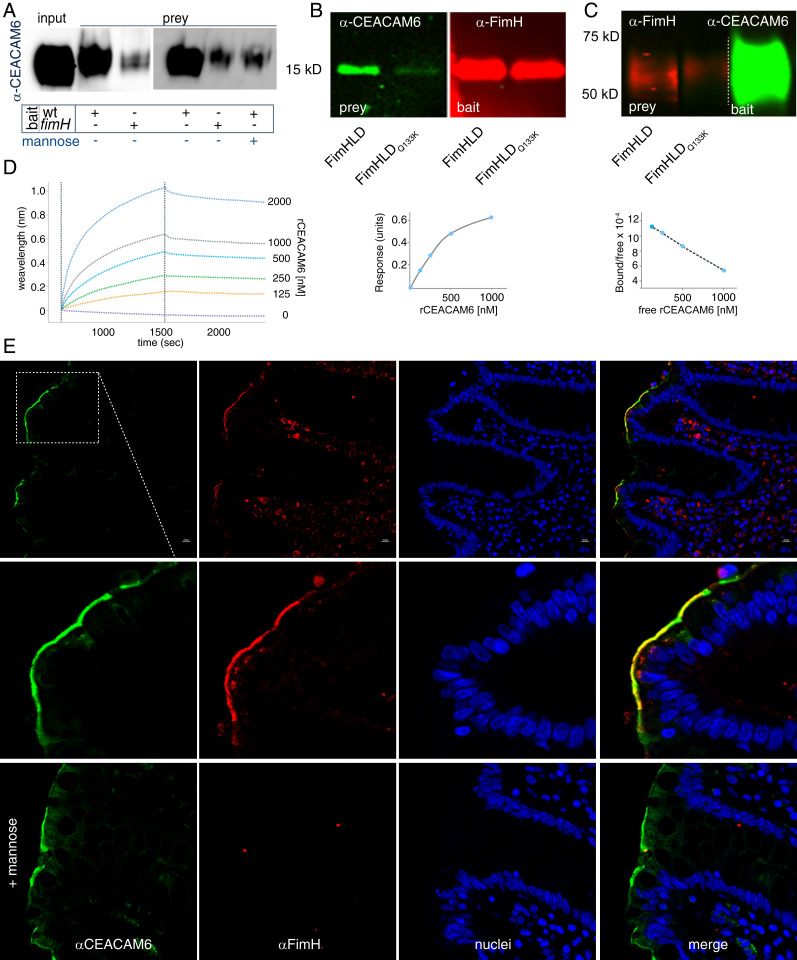
CEACAM6 interacts with the FimH tip adhesin of type 1 fimbriae. (A) FimH promotes interaction of CEACAM6 with ETEC. Anti-CEACAM6 immunoblot shows amount of CEACAM6 retained by wild type (wt) and fimH mutant ETEC following incubation of bacteria with recombinant CEACAM6 (rCEACAM6). (B, Left) CEACAM6 far Western blot (green) in which either FimHLD or the FimHLDQ133K mutant protein was used as bait. (Right) Immunoblot (red) shows relative amounts of protein transferred to the blot as bait. (C, Left) FimH far Western blot in which immobilized CEACAM6 is used as bait for FimH or the FimHLDQ133K mutant. (Right) Transferred rCEACAM6 used as bait is shown. (D) Biolayer interferometry studies demonstrate interaction between immobilized rFimH and varying concentrations of rCEACAM6. (E) rFimHLD colocalizes with CEACAM6 on human small intestinal biopsies in a mannose-dependent fashion.