Figure 2.
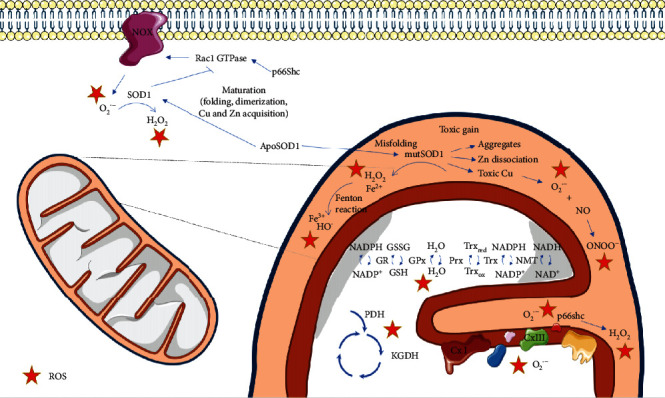
Mitochondrial dysfunction associated with SOD1 mutations. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) may be formed in several cellular reactions and are controlled by a network of antioxidant enzymes that include superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1), a Cu-Zn metalloprotein responsible for the conversion of O2•- into O2 and H2O2, which is mainly localized in the cytosol. SOD1 mutations are one of the most studied causes of ALS. Mutant SOD1 (mutSOD1) toxic gain involves its translocation to the mitochondrial intermembrane space, where it aggregates due to lower stability of mutSOD1 monomers/dimers.mutSOD1 may also cause elevated oxidative damage through the dissociation of zinc from the enzyme or exposure to toxic copper at the active site, promoting reverse O2•- production. O2•- reacts with nitric oxide generated by nitric oxide synthase, more rapidly than it does with SOD1, producing peroxynitrite, with consequent tyrosine nitration of cellular proteins. mutSOD1 may also act as a peroxidase by using H2O2 as a substrate, or the H2O2 produced in the dismutation reaction may originate HO• through the Fenton reaction. mutSOD1 may also induce the activation of p66Shc, a protein involved in controlling mitochondrial redox homeostasis. Outside mitochondria, mutSOD1 associates more strongly with Rac1 compared to the wild type form of SOD1, being less sensitive to redox uncoupling, consequently leading to an increase in NADPH oxidase- (NOX-) derived O2•-. ApoSOD1: metal-deficient Cu,Zn-superoxide dismutase; NADP: β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide 2′-phosphate; NADPH: β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide 2′-phosphate reduced form; NAD: β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NADH: β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide 2′-phosphate reduced form; GSH: reduced glutathione; GSSG: oxidized glutathione; Trxred: reduced Thioredoxin; Trxox: oxidized Thioredoxin; Trx: Thioredoxin, NMT: N-myristoyltransferase; Prx: peroxiredoxin; GPx: glutathione peroxidase; GR: glutathione reductase; PDH: pyruvate dehydrogenase; KGDH: alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase; CxI: complex I; CxIII: complex III.
