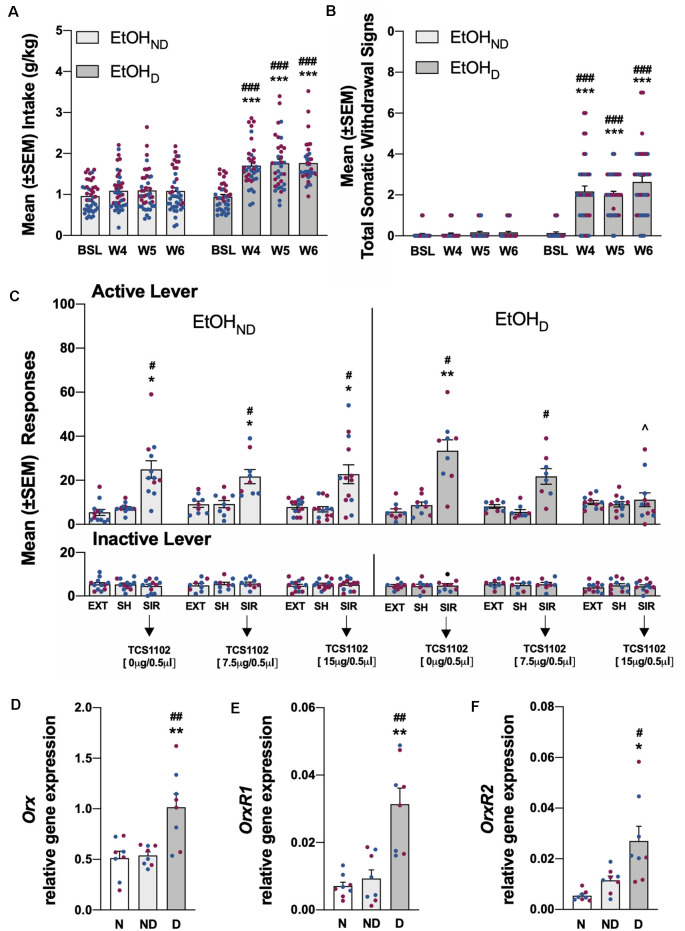
Figure 3.
(A) Total EtOH intake in the EtOHND and EtOHD groups during training and the air (EtOHND) and CIE (EtOHD) vapor procedure. ***p < 0.001, vs. training; ###p < 0.001, vs. EtOHND. n = 36–42 rats/group. (B) Somatic withdrawal signs (WDS) recorded upon the completion of training and during acute abstinence after CIE vapor exposure. ***p < 0.001, vs. baseline; ###p < 0.001, vs. EtOHND. n = 36–42 rats/group. (C) Effect of TCS1102 injection in the pPVT on footshock stress-induced reinstatement of EtOH-seeking behavior. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, vs. respective extinction and sham injection; ∧p < 0.05, vs. respective vehicle; #p < 0.05, vs. respective inactive lever. n = 8–13 rats/group. (D) Relative Orx gene expression in the hypothalamus in EtOH rats. **p < 0.01, vs. naive; ##p < 0.01, vs. EtOHND. (E) Relative OrxR1 gene expression in the pPVT in EtOH rats. **p < 0.01, vs. naïve; ##p < 0.01, vs. EtOHND. (F) Relative OrxR2 gene expression in the pPVT in EtOH rats. *p < 0.05, vs. naive; #p < 0.05, vs. EtOHND. Orx, OrxR1, and OrxR2 mRNA expression levels were normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Gapdh) and are expressed in relative amounts. n = 8 rats/group. Blue symbols indicate male rats. Purple symbols indicate female rats. BSL, baseline; W4, week 4; W5, week 5; W6, week 6; EXT, extinction; SH, sham injection; SIR, stress-induced reinstatement; N, naive; ND, EtOHND; D, EtOHD.