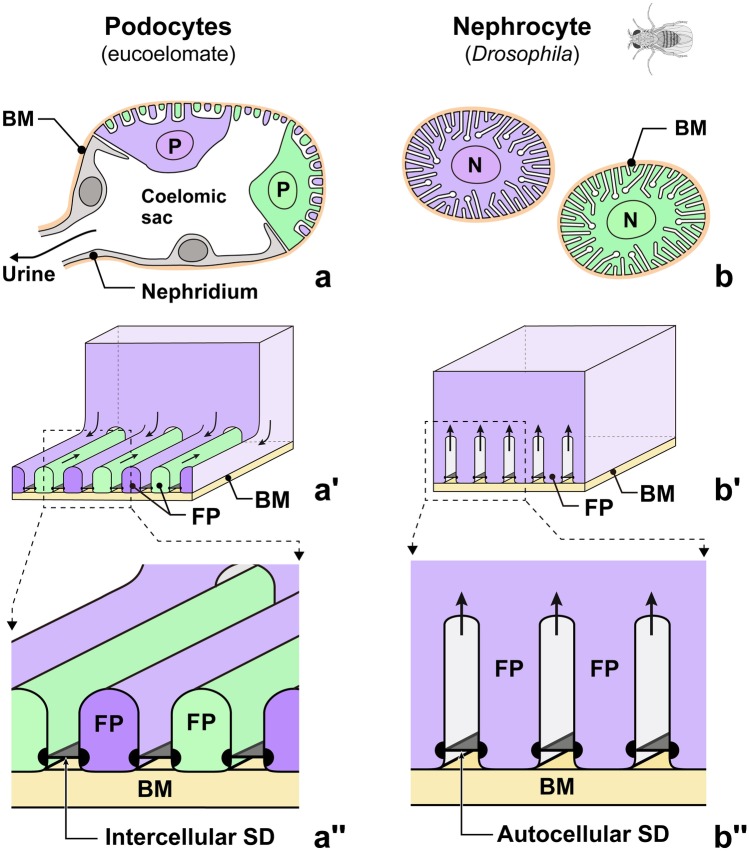
Fig. 1.
Structural difference between eucoelomate epithelium-forming podocytes and Drosophila solitary nephrocyte. (a–a″) Podocytes in eucoelomates. Podocytes (P) form a filtration epithelium, through which primary urine is produced (a) and excluded via a nephridium. Foot processes are formed by cytoplasmic protrusion from the cell's periphery and are interdigitated with those of adjacent podocytes (a′). Thus, podocyte slit diaphragms between foot processes are regarded as an intercellular junction (aʹʹ). (b–b″) Nephrocytes in fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster). Individual nephrocytes (N) are completely enwrapped by the basement membrane (brown). (b). Foot processes are formed by infolding of the basal plasma membrane (b′). Slit diaphragms are bridged between foot processes from the same nephrocyte, i.e., autocellular junction (b″). BM, basement membrane; FP, foot process; SD, slit diaphragm. Individual nephrocytes and podocytes are shown by different colors (purple and green)