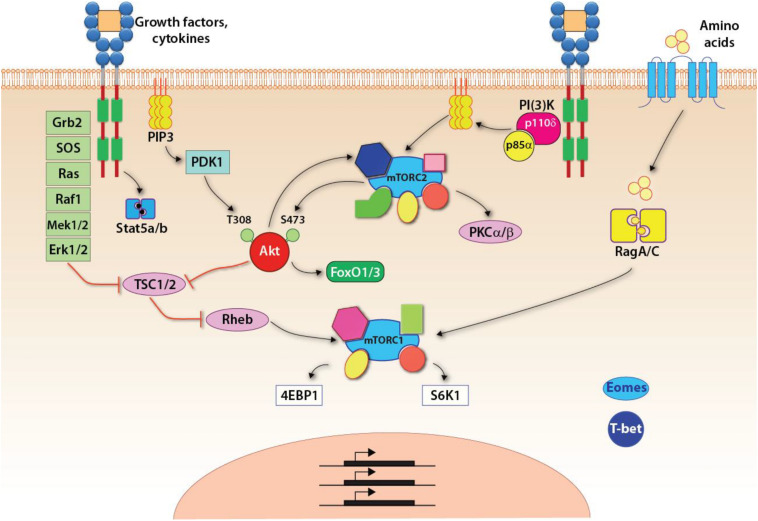
FIGURE 2.
Signaling pathways up and downstream of mTOR complexes. Upon growth factors- or cytokine-mediated activation, three major pathways are initiated: the Jak-Stat5 pathway, the PI(3)K-Akt-mTOR pathway, and the Ras-Raf-Mek-Erk1/2 MAPK pathway. Specific to the mTORC1 pathway, the tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) functions as a GTPase-activating protein (GAP), which inhibits the activity of Rheb, a small GTPase absolutely required for the activation of mTORC1. Thus, TSC is a central negative regulator of mTORC1 signaling. The activated Akt or Erk, downstream of PI(3)K-Akt or MAPK pathway, respectively, phosphorylates TSC and inhibits its GAP activity resulting in the activation of mTORC1. In addition, amino acids are required for anchoring mTORC1 on the lysosomal membrane where Rheb locates. This is achieved through the RagA/C.