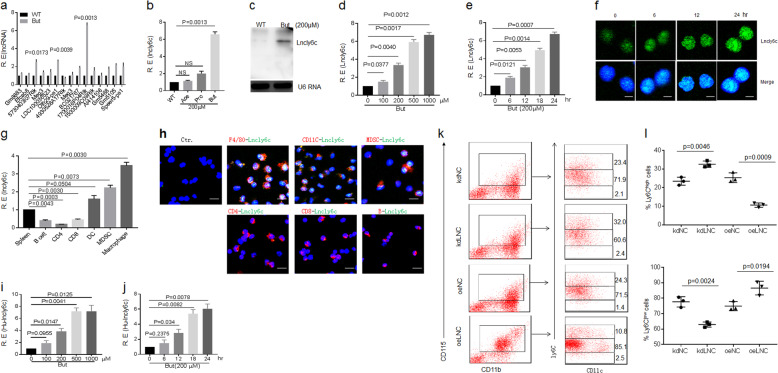
Fig. 2. Butyrate promotes expression of lncLy6C.
a QRT-PCR of lncRNAs in bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) after exposed to butyrate (200 μM). R. E relative expression. b QRT-PCR of lncLy6C in BMDMs after exposed to ascetic acid (200 μM), propionic acid (200 μM, and butyrate (200 μM). WT control vehicle, R. E relative expression. c Northern blot of lncLy6C in BMDMs after exposed to butyrate. WT control vehicle. d QRT-PCR of lncLy6C in BMDMs after exposed to different concentration of butyrate. R. E relative expression. e QRT-PCR of lncLy6C in BMDMs after exposed to butyrate (200 μM) at different time points. R. E relative expression. f FISH of lncLy6C in BMDMs after exposed to butyrate (200 μM) at different time points. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue); green, lncLy6C. Scale bar, 2.5 μM. g QRT-PCR of lncLy6C in spleen, B cell, CD4, CD8, dendritic cells (DC), myeloid-derived suppressive cells (MDSC), and macrophages sorted from spleen by flow cytometry. R. E relative expression. h FISH of lncLy6C and immunostaining of F4/80+, CD11c+, MDSC (ly6c+), CD4+, CD8+, and B (CD19+) cells in spleen. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue); green, lncLy6C. Scale bar, 40 μM. i QRT-PCR of lncLy6C in human CD14+ monocytes after exposed to different concentration of butyrate. R. E relative expression. j QRT-PCR of lncLy6C in human CD14+ monocytes after exposed to butyrate (200 μM) at different time points. R. E relative expression. k Flow cytometry of CD115+Ly6Chigh and CD115+Ly6Clow cells in lncLy6C microRNA (kdLNC) or lncLy6C (oeLNC) lentivirus transfected BMCs after culturing for 4 days in the presence of GM-CSF. KdNC control microRNA lentiviruses, oeNC control lentiviruses. l Comparison f Ly6Chigh and Ly6Clow cells in lncLy6C microRNA (kdLNC) or lncLy6C (oeLNC) lentivirus transfected BMCs and control microRNA (kdNC) or control lentivirus (oeNC) transfected BMCs, two-sided Student’s t test in a, b, d, e, g, i, j, and l; data for all panels are a representative from two to three experiments.